论文标题:Noninvasive sub-organ ultrasound stimulation for targeted neuromodulation
期刊:Nature Communications
作者:Victoria Cotero, Ying Fan, Tea Tsaava, Adam M. Kressel, Ileana Hancu, Paul Fitzgerald, Kirk Wallace, Sireesha Kaanumalle, John Graf, Wayne Rigby, Tzu-Jen Kao, Jeanette Roberts, Chitresh Bhushan, Suresh Joel, Thomas R. Coleman, Stavros Zanos, Kevin J. Tracey, Jeffrey Ashe, Sangeeta S. Chavan, Christopher Puleo
发表时间:2019/03/12
数字识别码: 10.1038/s41467-019-08750-9
原文链接:http://t.cn/EMgjVL6
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rO_PvayL5_T0UrsL-fcxTw
本周《自然-通讯》发表的两项研究Noninvasive sub-organ ultrasound stimulation for targeted neuromodulation和Noninvasive ultrasound stimulation of the spleen to treat inflammatory arthritis,展示了利用基于超声波的非侵入性方法来调节神经活动和治疗啮齿类动物模型的炎性关节炎和高血糖症,并且表明这种非药物学方法未来或可用于治疗炎症和代谢紊乱。
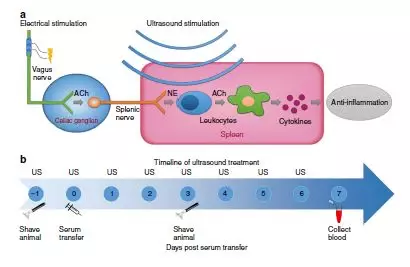
图1:通过迷走神经、脾神经和脾脏调节胆碱能抗炎通路。图源: Zachs 等
神经刺激可用于治疗一系列疾病,包括炎症、糖尿病和胃肠道疾病。然而,目前的方法需要植入电极,并且仅限于刺激大神经或靠近皮肤表面的神经。
美国明尼苏达大学的Daniel Zachs及其同事表明,每天对小鼠脾脏施用非侵入性超声波减轻了小鼠炎性关节炎的严重程度。他们还表明,该疗法引起了B细胞群和T细胞群的变化,而且在缺乏这些细胞的动物中治疗效果有所下降。
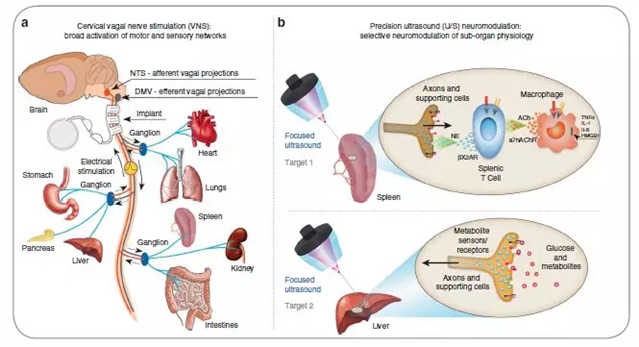
图2:对比利用植入物的VNS与精准的超声波神经调节。图源:Cotero等
在另一项使用大鼠和小鼠模型的独立研究中,美国GE全球研发中心的Chris Puleo、Vicky Cotero及其同事采用非侵入性方式对脾脏施用超声波,降低了小鼠和大鼠对细菌内毒素的炎症反应。通过这种方法取得的炎症缓解程度与使用利用植入物进行迷走神经刺激(VNS)的效果相似。他们发现使用超声波靶向肝脏时,这种调节通路会参与调节血糖水平,并且对于抑制高血糖以响应内毒素暴露的效果与VNS一致。不仅如此,他们还发现只有在靶向肝脏内已知包含葡萄糖感觉神经元的特定位置时,才会发生这种响应。
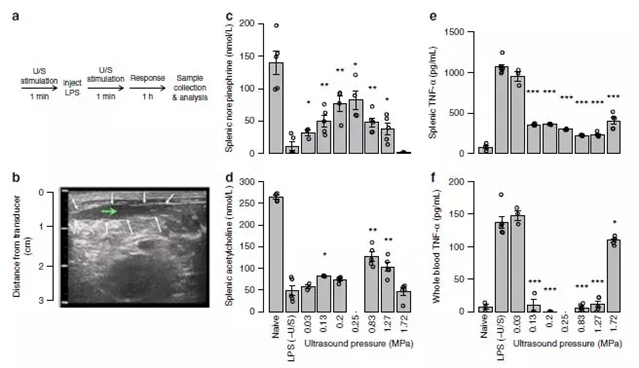
图3:胆碱能抗炎通路的超声波调节。图源:Cotero等
这两篇论文表明,超声刺激有望替代可植入装置,用于治疗适用于神经调节疗法的疾病。然而,非侵入性超声波对于类风湿性关节炎的应用潜力还需要进一步的研究,相关临床试验正在进行中。
摘要:Tools for noninvasively modulating neural signaling in peripheral organs will advance the study of nerves and their effect on homeostasis and disease. Herein, we demonstrate a noninvasive method to modulate specific signaling pathways within organs using ultrasound (U/S). U/S is first applied to spleen to modulate the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP), and US stimulation is shown to reduce cytokine response to endotoxin to the same levels as implant-based vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). Next, hepatic U/S stimulation is shown to modulate pathways that regulate blood glucose and is as effective as VNS in suppressing the hyperglycemic effect of endotoxin exposure. This response to hepatic U/S is only found when targeting specific sub-organ locations known to contain glucose sensory neurons, and both molecular (i.e. neurotransmitter concentration and cFOS expression) and neuroimaging results indicate US induced signaling to metabolism-related hypothalamic sub-nuclei. These data demonstrate that U/S stimulation within organs provides a new method for site-selective neuromodulation to regulate specific physiological functions.
阅读论文全文请访问:http://t.cn/EMgjVL6
期刊介绍:Nature Communications(https://www.nature.com/ncomms/) is an open access journal that publishes high-quality research from all areas of the natural sciences. Papers published by the journal represent important advances of significance to specialists within each field.
The 2017 journal metrics for Nature Communications are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 12.353
•5-year impact factor: 13.691
•Immediacy index: 1.829
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.92656
•Article Influence Score: 5.684
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。