论文标题:Accelerated vortex dynamics across the magnetic 3D-to-2D crossover in disordered superconductors
期刊:npj Quantum Materials
作者:Serena Eley et al
发表时间: 2018/8/17
数字识别码:10.1186/ s41535-018-0108-1
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41535-018-0108-1?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Email_InternalWebsite_links&utm_content=JesGuo-Nature-npj_Quantum_Materials-Materials_Physics-China&utm_campaign=NPJ_USG_JRCN_JG_NPJ_3Dto2D
超导体:涡旋和缺陷的作用
在超导体中,由于缺陷会钉扎涡旋,所以无序的结构会影响超导体的性质。热能可以释放涡旋,其蠕变速率取决于样品厚度,特别是当样品厚度减小到钉扎长度以下时。然而,在具有不同类型缺陷的系统中,关于钉扎的描述仍然存在争论。来自美国洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室的Serena Eley及其同事们系统地研究了铌(Nb,超导临界温度Tc=9.2 K)和铜氧化物材料(Tc=92 K)薄膜的涡旋蠕变速率对厚度的依赖性。结果表明在这些材料中,缺陷对于钉扎涡旋具有不同的作用,同时,结果也表明这种方法提供了一种直接获得非均匀无序材料(如铜氧化物)中钉扎长度的方法。
摘要
在超导体中,无序的结构会产生明显不同的结果,通过定位电子对来驱动超薄膜中的超导体——绝缘体转变,通过定位涡旋(磁通量线)来提高厚膜的超电流承载能力。虽然电子由3D到2D的交叉过程在材料厚度~相干长度(d ~ ξ )方面获得了很好的研究,但同样重要的磁性交叉在材料厚度~钉扎长度(d~Lc)方面应该能够很大程度上改变材料特性远未得到充分验证。根据集体钉扎理论,长度为Lc的涡旋段可以调整到由点缺陷提供的能量井。因此,如果d截断Lc,从弹性到刚性涡旋动力学的变化应该会增加热激活涡旋运动的速率S。本论文中,我们在铌和铜氧化物薄膜中表征了S对样品厚度的依赖性。 其中,铌的表征结果与集体钉扎理论一致,而铜氧化物中的蠕变受到稀疏大沉淀物的严重影响。我们利用S与d之间灵敏度的关系来确定通常未知的标度Lc,从而建立了一种在非均匀无序材料中提取钉扎长度的新方法。
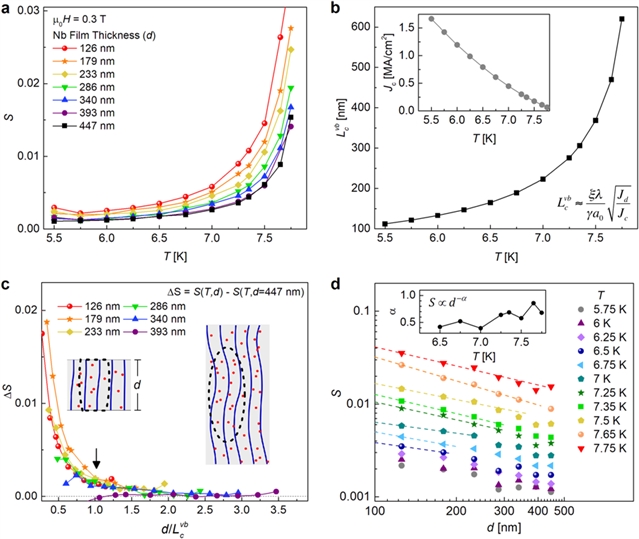
铌薄膜中厚度依赖性的涡旋蠕变
摘要:
Disorder can have remarkably disparate consequences in superconductors, driving superconductor–insulator transitions in ultrathin films by localizing electron pairs and boosting the supercurrent carrying capacity of thick films by localizing vortices (magnetic flux lines). Though the electronic 3D-to-2D crossover at material thicknesses d ~ ξ (coherence length) is well studied, a similarly consequential magnetic crossover at d ~ Lc (pinning length) that should drastically alter material properties remains largely underexamined. According to collective pinning theory, vortex segments of length Lcbend to adjust to energy wells provided by point defects. Consequently, if d truncates Lc, a change from elastic to rigid vortex dynamics should increase the rate of thermally activated vortex motion S. Here, we characterize the dependence of S on sample thickness in Nb and cuprate films. The results for Nb are consistent with collective pinning theory, whereas creep in the cuprate is strongly influenced by sparse large precipitates. We leverage the sensitivity of S to d to determine the generally unknown scale Lc, establishing a new route for extracting pinning lengths in heterogeneously disordered materials.
阅读论文原文,请访问
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41535-018-0108-1?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Email_InternalWebsite_links&utm_content=JesGuo-Nature-npj_Quantum_Materials-Materials_Physics-China&utm_campaign=NPJ_USG_JRCN_JG_NPJ_3Dto2D
(来源:科学网)