论文标题:Impacts of glass composition, pH, and temperature on glass forward dissolution rate
期刊:npj Materials Degradation
作者:John D. Vienna et al
发表时间: 2018/8/6
数字识别码:10.1186/ s41529-018-0042-5
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41529-018-0042-5?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_linksWebsite_links&utm_content=JesGuo-Nature-npj_Materials_Degradation-Materials_Science_of_Composites-China&utm_campaign=NPJ_USG_JRCN_JG_NPJ_Impacts
玻璃溶解:理解结构效应
本文研究了环境和玻璃成分对水溶液中核废料储存玻璃腐蚀速率的影响。 硼硅酸盐玻璃通常被用作处理放射性废物的隔离基质。它们通过与水的相互作用,可以释放自身装载的放射性物质,因此了解玻璃腐蚀的条件非常重要。目前,来自西北太平洋国家实验室的John Vienna及其同事们,他们研究了pH值,温度和玻璃成分对各种玻璃溶解速率的影响。通过测量某一种待测玻璃的溶解速率,将其与其他玻璃进行比较,结合一些建模模拟,他们发现90%的溶解速率的变化可以通过温度和pH效应来解释 - 因此任何成分影响相对较小。
摘要
核废料玻璃在非常稀的水溶液中以正向溶解速率(rf)溶解,这可以隔离玻璃成分对溶液反馈和蚀变产物效应的影响。虽然长期以来人们都知道pH值和温度(T)对rf有强烈影响,但玻璃成分带来的影响尚不明确。在本项工作中,为了确定玻璃成分对rf 的影响,我们采用了来自19种核废料玻璃的rf 数据。rf 值被建模为:rf = k010–ηpHexp(−Ea/RT),其中k0, η, Ea, 和R分别为固有速率常数,pH系数,表观活化能和气体常数。然而,在本研究中,所采用玻璃的各个模型参数(log[k0], η, 和 Ea)和玻璃成分之间并不存在预测相关性,这一结果归因于log[k0]和Ea之间的强正相关性。因此,19种玻璃组合得到的 rf 可以直接拟合出一个模型。 这种方法表明, 90%的rf 的变化可以仅通过T和pH效应来解释。因此任何成分的影响都必定相对较小。在对pH值和 T的差异进行归一化后发现,不同玻璃之间 rf值的显著差异与由硼四面体f([4]B)形成的玻璃四面体的组分变化相关,并且在一处高值 f([4]B) (~0.22)处出现突然的阈值,在此处,预测可得到更高的 rf ,且在阈值以下没有可辨别的结构效应。
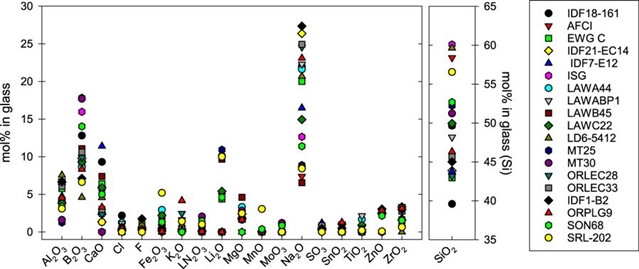
玻璃成分组(成分的摩尔分数)。 “LN 2 O 3”为组合的镧系氧化物
Abstract:
Nuclear waste glasses dissolve at the forward dissolution rate (rf) in very dilute aqueous solutions, which can isolate the impact of the glass composition from solution feedback and alteration product effects. While it has long been known that pH and temperature (T) strongly impact rf, the impacts of glass composition have remained uncertain. In this work, rf data from 19 nuclear waste glasses were used with the aim of identifying the effect of glass composition on rf. The rf values were modeled as: rf = k010–ηpHexp(−Ea/RT), with k0, η, Ea, and R, respectively, being the intrinsic rate constant, pH coefficient, apparent activation energy, and gas constant. However, no predictive correlation could be established between the individual model parameters (log[k0], η, and Ea) and glass composition for the glasses considered in this study, an outcome that was attributed to the strong positive correlation between the log[k0] and Ea parameters. Therefore, a model was fitted directly to the combined rf from all 19 glasses. This approach showed that 90% of the variation in rf data could be accounted for solely by T and pH effects. Therefore, any composition effects must be relatively small. After normalizing for differences in pH and T, the only notable differences in rf between the glasses were found to correlate with variations in the fraction of glass forming tetrahedra contributed by tetrahedral boron, f([4]B), with an abrupt threshold at a high value of f([4]B) (~0.22), where higher rf are predicted with no discernable composition effects below the threshold.
阅读论文原文,请访问
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41529-018-0042-5?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_linksWebsite_links&utm_content=JesGuo-Nature-npj_Materials_Degradation-Materials_Science_of_Composites-China&utm_campaign=NPJ_USG_JRCN_JG_NPJ_Impacts
(来源:科学网)