|
|
| 分析营养健全的植物性饮食与肉食的影响 |《科学报告》 |
|
论文标题:Environmentally Optimal, Nutritionally Sound, Protein and Energy Conserving Plant Based Alternatives to U.S. Meat
期刊:Scientific Reports
作者:Gidon Eshel,Paul Stainier,Alon Shepon,Akshay Swaminathan
发表时间:2019/08/08
数字识别码:10.1038/s41598-019-46590-1
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Q5x5_UGOSu2K3nhHSJJsVw
使用含有蛋白质的植物代替肉食,仍能满足美国人的关键营养需求,还可以废除牧场的使用,并将目前粮食生产所需的耕地减少35-50%。以上发现来自《科学报告》发表的一项模型研究Environmentally Optimal, Nutritionally Sound, Protein and Energy Conserving Plant Based Alternatives to U.S. Meat,研究表明氮肥和温室气体排放量也将减少,而只有粮食相关的用水会增加。
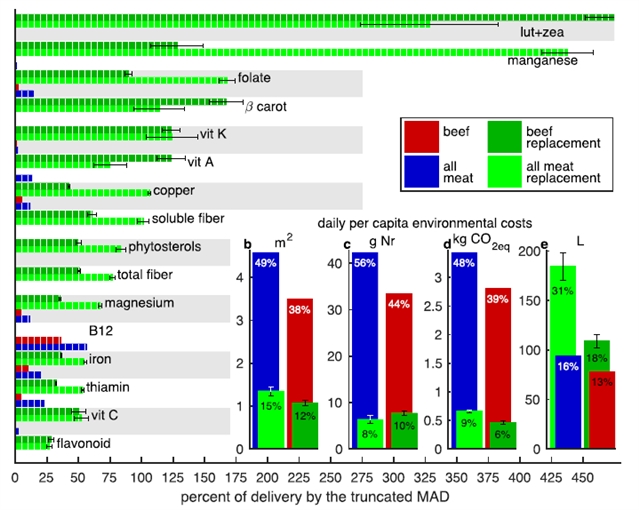
图1 使用营养健全的植物性饮食代替肉食对关键营养和环境的影响 图源:Eshe等
美国巴德学院的Gidon Eshel及同事使用计算机模型设计了数百种植物性食品,用以只取代牛肉或取代美国全部三种主要肉类:牛肉、家禽肉和猪肉。这类植物性食品的成分主要包括大豆、青椒、南瓜、荞麦和芦笋。作者的目标是模拟一系列和肉类至少具有同等营养价值——甚至可能更有营养——的植物性食物,并且评估它们的环境影响。模拟的植物性食品严格匹配其所代替肉类的蛋白质含量——牛肉每天13克蛋白质或者所有三种肉类总计每天30克蛋白质;同时亦满足另外43种营养物质要求,比如维生素和脂肪酸。
在用以代替全部肉类的植物性饮食中,荞麦和豆腐提供了其中全部蛋白质的三分之一,但是只占生产这些肉类所需氮肥与用水的12%,占所需耕地的不到22%。在代替牛肉的植物性食品中,大豆提供了最多的蛋白质,但是只占生产牛肉所需的全部氮肥的6%。据估计,用植物性食品代替肉类每年可以使美国节约2900万公顷左右的耕地、30亿千克的氮肥,并且减少2800亿千克的二氧化碳排放;而食物相关用水预计将增加15%。
摘要:Because meat is more resource intensive than vegetal protein sources, replacing it with efficient plant alternatives is potentially desirable, provided these alternatives prove nutritionally sound. We show that protein conserving plant alternatives to meat that rigorously satisfy key nutritional constraints while minimizing cropland, nitrogen fertilizer (Nr) and water use and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions exist, and could improve public health. We develop a new methodology for identifying nutritional constraints whose satisfaction by plant eaters is challenging, disproportionately shaping the optimal diets, singling out energy, mass, monounsaturated fatty acids, vitamins B3,12 and D, choline, zinc, and selenium. By replacing meat with the devised plant alternatives—dominated by soy, green pepper, squash, buckwheat, and asparagus—Americans can collectively eliminate pastureland use while saving 35–50% of their diet related needs for cropland, Nr, and GHG emission, but increase their diet related irrigation needs by 15%. While widely replacing meat with plants is logistically and culturally challenging, few competing options offer comparable multidimensional resource use reduction.
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。