|
|
| 利用体外器官支持系统让受损猪肺再生 | 《自然-通讯》 |
|
论文标题:Regeneration of severely damaged lungs using an interventional cross-circulation platform
期刊:Nature Communications
作者:Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O’Neill, Jinho Kim, Dawn Queen, Scott Chicotka, Kenmond Fung, Michael Simpson, Rachel Donocoff, Michael Salna, Charles C. Marboe, Katherine Cunningham, Susan P. Halligan, Holly M. Wobma, Ahmed E. Hozain, Alexander Romanov, Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic, Matthew Bacchetta
发表时间:2019/05/07
数字识别码: 10.1038/s41467-019-09908-1
原文链接:http://t.cn/EoHK9OF
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Qu__62StqjtFBN-JXqBf7Q
《自然-通讯》本周发表的一篇论文Regeneration of severely damaged lungs using an interventional cross-circulation platform报道了利用体外器官支持系统让受损猪肺再生。初步结果显示,受损后的猪肺或能进行修复,并用于器官移植。
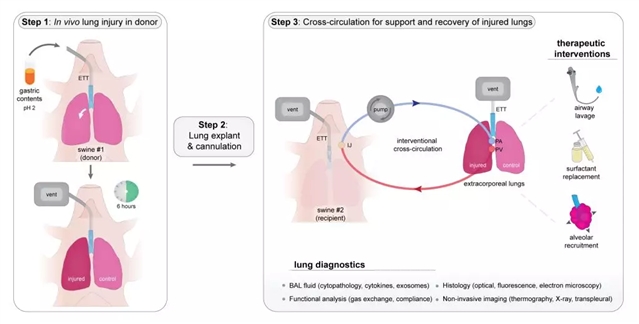
图1:实验中先用胃内容物吸入造成损伤,再以交叉循环系统恢复再生这一供体器官。
图源:Dr. Brandon Guenthart
胃内容物吸入是指胃内物质进入呼吸道,这种常见损伤会导致肺脏无法用于移植。鉴于现在全球都面临着移植供体短缺的问题,受损肺脏再生技术有望扩充适合移植的器官库。
美国范德堡大学的Matthew Bacchetta和同事研究了严重受损肺脏再生后达到移植标准的可能性。作者在8只猪的体内再现了胃内容物吸入性损伤,并通过体外支持系统将受损肺脏与受体动物的循环系统相连,对器官进行维持。利用这一交叉循环系统,供体肺在猪体外最长能维持36个小时,让一系列治疗干预措施得以进行。该系统不仅能让受损肺脏再生,还能提高其功能,且再生后的肺脏满足所有移植条件。
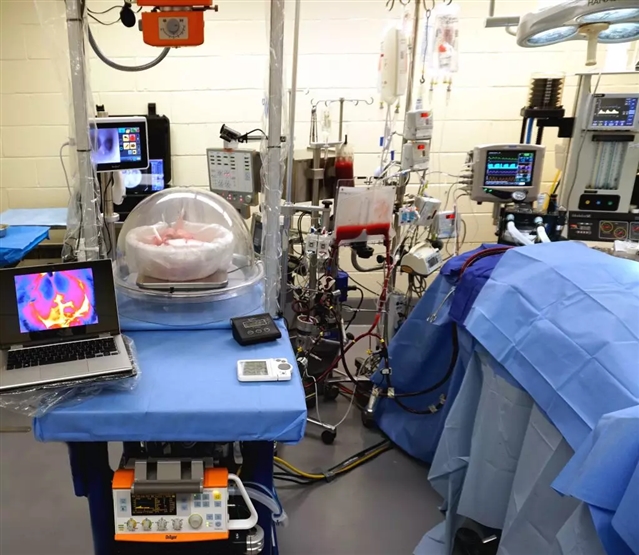
图2:正在进行中的交叉循环干预过程。图源:Dr. Brandon Guenthart
还需开展进一步研究确定肺移植后的功能肺活量以及该方法的安全性。由于人体内的器官移植必须接受免疫抑制治疗,未来还应对免疫抑制对肺恢复的影响做进一步评估。
摘要:The number of available donor organs limits lung transplantation, the only lifesaving therapy for the increasing population of patients with end-stage lung disease. A prevalent etiology of injury that renders lungs unacceptable for transplantation is gastric aspiration, a deleterious insult to the pulmonary epithelium. Currently, severely damaged donor lungs cannot be salvaged with existing devices or methods. Here we report the regeneration of severely damaged lungs repaired to meet transplantation criteria by utilizing an interventional cross-circulation platform in a clinically relevant swine model of gastric aspiration injury. Enabled by cross-circulation with a living swine, prolonged extracorporeal support of damaged lungs results in significant improvements in lung function, cellular regeneration, and the development of diagnostic tools for non-invasive organ evaluation and repair. We therefore propose that the use of an interventional cross-circulation platform could enable recovery of otherwise unsalvageable lungs and thus expand the donor organ pool.
阅读论文全文请访问:http://t.cn/EoHK9OF
期刊介绍:Nature Communications(https://www.nature.com/ncomms/) is an open access journal that publishes high-quality research from all areas of the natural sciences. Papers published by the journal represent important advances of significance to specialists within each field.
The 2017 journal metrics for Nature Communications are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 12.353
•5-year impact factor: 13.691
•Immediacy index: 1.829
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.92656
•Article Influence Score: 5.684
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。