论文标题:The associations between smoking and obesity in northeast China: a quantile regression analysis
期刊:Scientific Reports
作者:Mengzi Sun, Yan Jiang, Chong Sun, Jiagen Li, Xin Guo, Yaogai Lv, Yaqin Yu, Yan Yao, Lina Jin
发表时间:2019/03/14
数字识别码: 10.1038/s41598-019-39425-6
原文链接:http://t.cn/ExkfxeA
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/aG2bSbPDoySmHWaNlkiAVA
本周《科学报告》发表的一项研究The associations between smoking and obesity in northeast China: a quantile regression analysis指出,与非吸烟者相比,吸烟者的腰围更大,即便他们的BMI(身高体重指数)可能比非吸烟者还要低一些。这些研究结果表明,抽烟可能会导致腹部脂肪的堆积,哪怕体重并未增加。

图1 图源: Pixabay
吉林大学的金丽娜及同事分析了来自中国吉林省的16142个吸烟者与非吸烟者的数据,以探索吸烟与肥胖之间的关系,其中吸烟者的定义为一生中抽烟数至少达到100根且仍在抽烟的人。与非吸烟者相比,吸烟者的BMI更小,腰围也更小。但进一步的分析显示,在BMI相同的情况下,吸烟者的腰围比非吸烟者更大。并且随着腰围的增长,腰围与吸烟之间的这种关联会越来越强,尤其是在女性中。这可能意味着一个人腰围越大,吸烟对他/她的影响越强烈,而腰围较大的女性尤为需要戒烟干预。
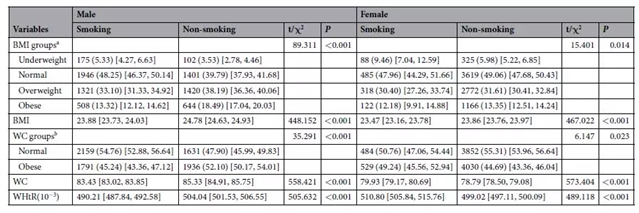
图2:不同性别和吸烟情况人群的BMI和腰围分布。图源:Sun等
本研究的所有参与者都来自中国东北的吉林省。吉林的超重、肥胖和吸烟比例分别为32.3%,14.6%和39.1%,这些数字远高于全中国的平均水平,因此吉林较为适合研究吸烟与肥胖。但是作者也提醒,由于所有结果均来自同一个省份的人群数据,可能无法完全推广到其他人群中。
摘要:Obesity is a risk factors of chronic diseases, and smoking is associated with both chronic diseases and obesity. There were some controversies about the associations between smoking and obesity. Thus, our study aimed to explore the associations of smoking with obesity, using body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) as obesity indices in northeast China. We enrolled a sample of 16,412 participants in Jilin province aged 18–79 in this study, which were derived from a cross-sectional survey in 2012. We used quantile regression (QR) models to identify the associations of smoking with obesity in different quantiles of BMI (or WC) by genders. The differences of BMI and WC by genders were statistically significant (p < 0.05). In conclusion, compared with current non-smokers, current smokers had lower BMI but higher WC. As increasing of WC, the association of WC with smoking was getting stronger, especially in females.
阅读论文全文请访问:http://t.cn/ExkfxeA
期刊介绍:Scientific Reports (https://www.nature.com/srep/) is an online, open access journal from the publishers of Nature. We publish scientifically valid primary research from all areas of the natural and clinical sciences.
The 2017 journal metrics for Scientific Reports are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 4.122
•5-year impact factor: 4.609
•Immediacy index: 0.576
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.71896
•Article Influence Score: 1.356
•2-year Median: 2
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。