|
|
| TrkAIII与人类恶性肿瘤的相关性 | BMC Journal |
|
论文标题:The oncogenic neurotrophin receptor tropomyosin-related kinase variant, TrkAIII
期刊:Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
作者:Antonietta Rosella Farina, Lucia Cappabianca, Pierdomenico Ruggeri, Luciana Gneo, Cristina Pellegrini, Maria-Concetta Fargnoli and Andrew Reay Mackay
发表时间:2018/06/18
数字识别码:10.1186/s13046-018-0786-3
原文链接:https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13046-018-0786-3?utm_source=BMC_mailing&utm_medium=Email_Internal&utm_content=EvaFon-BMC-Journal_of_Experimental_and_Clinical_Cancer_Research-Oncology-Global&utm_campaign=AJH_AWA_JECCR_10th_Anniversary#Abs1
微信链接:http://live.weibo.com/show?id=1042152:d2685057af9d604ddff16da521cca86a
Antonietta Rosella Farina等作者在Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research上在线发表了一篇综述:The oncogenic neurotrophin receptor tropomyosin-related kinase variant, TrkAIII。在这篇综述中作者介绍了神经营养因子受体原肌球蛋白相关激酶变体(TrkAIII)的检测及其与人类恶性肿瘤相关性的研究进展,包括:TrkAIII的检测、TrkAIII与人类恶性肿瘤的相关性、TrkAIII发挥致癌活性的机制,以及表达TrkAIII的肿瘤种类,尤其介绍了神经母细胞瘤的潜在治疗策略。
在许多正常的组织中,神经营养因子受体原肌球蛋白相关激酶A (TrkA) 调节着对神经营养因子NGF和NT3的应答过程。并且TrkA对于神经和免疫系统的正常运转和发育至关重要。
TrK癌基因是人类第一个TrkA来源的癌基因,在结肠癌中被首次发现。当时定义它是一种新的嵌合物(融合了截短的原肌球蛋白和酪氨酸蛋白激酶序列)。后来,TrKA原癌基因被定义为NGF受体,并且在许多人类癌症中均鉴定出许多TrKA来源的癌基因。现在,普遍认为TrKA是多种人类癌症亚群中的重要驱动因素,因此它是重要的癌症治疗靶点。
TrKA除了能驱动肿瘤的形成,最新的一项研究结果表明:TrK家族的抑制剂Larotrectinib对新型TrkA嵌合物所驱动的成人和儿童肿瘤具有显著、持续的抑制效果。这进一步强调了需要进一步优化由TrkA的致癌基因所驱动的癌症的临床检测,从而得以最大限度地发挥这种新型治疗方案的潜力。
Antonietta Rosella Farina等人总结了可能由TrkA癌基因所驱动的肿瘤,包括一些表达TrkA剪切变体TrkAIII的儿童神经母细胞瘤(NB)。TrkAIII相较于TrkA,区别在于外显子6,7的9跳跃,以及细胞外D4 Ig样结构域的缺失所造成的致癌活性。与此形成对比的是,完全剪切的TrkA在神经母细胞瘤中表现出肿瘤抑制作用,且与良好预后息息相关。而TrkAIII则与晚期转移性疾病、治疗后复发以及不良预后相关,还可诱导NIH-3T3细胞的恶变并在神经母细胞瘤模型中表现出致癌活性(图1)。
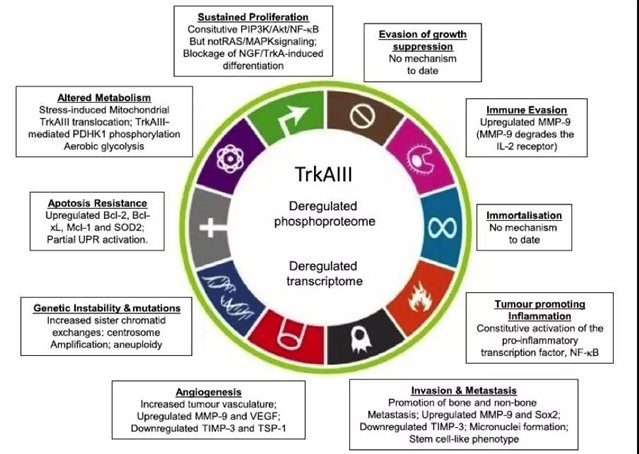
图1:TrkAlll对绝大多数的癌症功能特质均有影响(例如:TrkAlll下调磷酸化蛋白质组和转录组)。
图源:Andrew Reay Mackay 等
TrkAIII在神经母细胞瘤中的诱发主要受模拟缺氧和干扰内质网的应激调节,这有可能在应激性肿瘤微环境中将TrkA的肿瘤抑制信号转变为TrkAIII的致癌信号。TrkA主要位于细胞表面,而TrkAIII一旦表达,则重新定位于细胞内高尔基体前膜、中心体和线粒体。在这些细胞器内,TrkAIII会出现非配体依赖的自发性激活,通过多种机制促进肿瘤发生和恶性生物学行为,影响大多数肿瘤特征(图2)。

图2:TrkAIII的肿瘤表现和致癌机制以及针对表达TrkAIII肿瘤的潜在治疗因子和其他治疗方案。
图源:Andrew Reay Mackay 等
作者最后指出,对于对TrkAIII的活性、表达、下游信号传导有潜在抑制效果的治疗因子,单独使用这些治疗因子或者与基因毒性应激,氧化应激以及内质网干扰应激所诱导的肿瘤药物联合作用,可能对表达TrkAIII的癌症有更好的治疗效果。
摘要:Oncogenes derived from the neurotrophin receptor tropomyosin-related kinase TrkA act as drivers in sub-populations of a wide-range of human cancers. This, combined with a recent report that both adult and childhood cancers driven by novel oncogenic TrkA chimeric-fusions exhibit profound, long-lived therapeutic responses to the Trk inhibitor Larotrectinib, highlights the need to improve clinical detection of TrkA oncogene-driven cancers in order to maximise this novel therapeutic potential. Cancers potentially driven by TrkA oncogenes include a proportion of paediatric neuroblastomas (NBs) that express the alternative TrkAsplice variant TrkAIII, which exhibits exon 6, 7 and 9 skipping and oncogenic-activity that depends upon deletion of the extracellular D4 Ig-like domain. In contrast to fully spliced TrkA, which exhibits tumour suppressor activity in NB and associates with good prognosis, TrkAIII associates with advanced stage metastatic disease, post therapeutic relapse and worse prognosis, induces malignant transformation of NIH-3T3 cells and exhibits oncogenic activity in NB models. TrkAIII induction in NB cells is stress-regulated by conditions that mimic hypoxia or perturbate the ER with potential to change TrkA tumour-suppressing signals into oncogenic TrkAIII signals within the stressful tumour microenvironment. In contrast to cell surface TrkA, TrkAIII re-localises to intracellular pre-Golgi membranes, centrosomes and mitochondria, within which it exhibits spontaneous ligand-independent activation, triggering a variety of mechanisms that promote tumorigenicity and malignant behaviour, which impact the majority of cancer hallmarks. In this review, we present updates on TrkAIII detection and association with human malignancies, the multiple ways TrkAIII exerts oncogenic activity and potential therapeutic approaches for TrkAIII expressing cancers, with particular reference to NB.
阅读论文全文请访问:https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13046-018-0786-3?utm_source=BMC_mailing&utm_medium=Email_Internal&utm_content=EvaFon-BMC-Journal_of_Experimental_and_Clinical_Cancer_Research-Oncology-Global&utm_campaign=AJH_AWA_JECCR_10th_Anniversary#Abs1
期刊介绍:Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research(https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/) is an online peer-reviewed journal that publishes original research papers, reviews and commentaries in cancer research, from bench to bedside.
2017 Journal Metrics
Citation Impact
6.217 - 2-year Impact Factor
5.280 - 5-year Impact Factor
1.350 - Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP)
2.000 - SCImago Journal Rank (SJR)
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。