论文标题:In-orbit operation of an atomic clock based on laser-cooled 87Rb atoms
期刊:Nature Communications
作者:Liang Liu, De-Sheng Lü, Wei-Biao Chen et al
发表时间: 2018/07/24
数字识别码:10.1038/s41467-018-05219-z
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05219-z?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-Nature-Nature_Comms-Physics_of_Atomic_of_Molecular_and_Chemical-China&utm_campaign=NATCOMMS_USG_JRCN_RL_atoms_sciencenet_article_1st_Aug
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/c_9LZrHScSZ80qqSRRWOLg

《自然-通讯》论文In-orbit operation of an atomic clock based on laser-cooled 87Rb atoms介绍了一种能够在太空运行的冷原子钟。研究表明,冷原子可以用作稳定的在轨时钟,有望用于计量学以及测试一些基本的物理学原理。
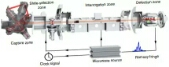
图1:太空冷原子钟的原理和结构。图源:Liu et al.
原子钟根据两个原子能级之间的能量差计时。冷原子的这种能量差可以通过激光探测进行精确测量,而且在实验室条件下,冷原子钟可以不受外部扰动,保持稳定。然而,要使这种时钟在太空长期运行仍具有挑战性,因为来自地球辐射带的磁场扰动和高能粒子会影响它的稳定性。
现在,中科院光学精密机械研究所的刘亮及其同事报告了冷原子钟稳定在轨运行的证据。他们在微重力环境下囚禁并冷却铷原子,使用微波和激光脉冲探测它们。他们在微波与原子相互作用后检测原子在能级上的布居数,发现在轨时钟的稳定性为十万亿之三。
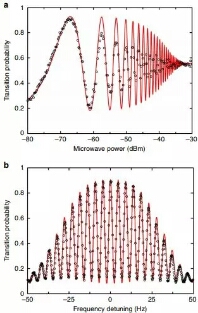
图2:微波探测后的原子数振荡。图源:Liu et al.
这些在恶劣的微重力环境下仍能可靠运行的稳定冷原子钟可用于开发空间计量传感器,测试基本常数的变化、广义相对论和爱因斯坦等效原理。
摘要:Atomic clocks based on laser-cooled atoms are widely used as primary frequency standards. Deploying such cold atom clocks (CACs) in space is foreseen to have many applications. Here we present tests of a CAC operating in space. In orbital microgravity, the atoms are cooled, trapped, launched, and finally detected after being interrogated by a microwave field using the Ramsey method. Perturbing influences from the orbital environment on the atoms such as varying magnetic fields and the passage of the spacecraft through Earth’s radiation belt are also controlled and mitigated. With appropriate parameters settings, closed-loop locking of the CAC is realized in orbit and an estimated short-term frequency stability close to 3.0 × 10−13τ−1/2 has been attained. The demonstration of the long-term operation of cold atom clock in orbit opens possibility on the applications of space-based cold atom sensors.
阅读论文全文请访问:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05219-z?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-Nature-Nature_Comms-Physics_of_Atomic_of_Molecular_and_Chemical-China&utm_campaign=NATCOMMS_USG_JRCN_RL_atoms_sciencenet_article_1st_Aug
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。