论文标题:Continuous-wave multiphoton photoemission from plasmonic nanostars
期刊:Communications Physics
作者:Murat Sivis et al
发表时间:2018/04/19
数字识别码:10.1038/s42005-018-0014-7
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s42005-018-0014-7?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-Nature-Communications_Physics-Optics/Lasers-China&utm_campaign=NEWCOMMS_USG_JRCN_RL_sciencenet_nanostars_Aug_3rd
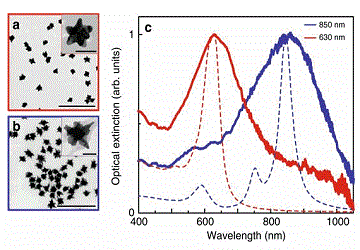
《通讯-物理学》发表的一项成果Continuous-wave multiphoton photoemission from plasmonic nanostars 研究了单个等离激元金纳米星的非线性光电发射现象。
高度非线性光学过程需要高的光强度,通常是用超短激光脉冲实现的。也正因此,皮秒激光技术出现之后,高度非线性光学过程才被首次观测到。特定等离激元纳米结构中的局域光学共振效应,提供了一种达到所需场强的替代方案,并可增强大量的非线性现象。然而,至今为止,通过等离激元增强的高阶非线性效应仅限于使用短脉冲和超快激光源的实验。来自德国哥廷根大学的Murat Sivis和西班牙巴塞罗那科学技术学院的F. Javier García de Abajo及其同事,展示了在亚MWcm−2级大小的入射光强度的连续波照明下,化学合成的等离激元金纳米星的局域三光子的光电发射现象。对光的强度和偏振的依赖性测量证实了光电发射过程的非线性,并与量子力学计算的尺寸小于5 nm 的纳米星探针所得到的电子产量相一致,使得局部强度增强因子超过1000。该研究成果为可及纳米级相干电子源的设计开辟了新的途径,并在显微镜、光谱、传感以及信号处理方面有潜在的应用前景。
摘要:Highly nonlinear optical processes require high intensities, typically achieved with ultrashort laser pulses, and hence, they were first observed with the advent of picosecond laser technology. An alternative approach for reaching the required field intensities is offered by localized optical resonances in tailored plasmonic nanostructures, enabling the enhancement of a multitude of nonlinear phenomena. However, so far, plasmon-enhanced high-order nonlinear effects have been restricted to experiments involving short-pulsed and ultrafast laser sources. Here, we demonstrate localized three-photon photoemission from chemically synthesized plasmonic gold nanostars under continuous-wave illumination at sub-MWcm−2 incident intensities. Intensity- and polarization-dependent measurements confirm the nonlinearity of the photoemission process and agree with quantum mechanical calculations of the electron yield from nanostar tips with features smaller than 5 nm, which facilitate local intensity enhancement factors exceeding 1000. Our results open up new avenues for the design of accessible nanoscale coherent electron sources, with potential applications in microscopy, spectroscopy, sensing, and signal processing.
阅读论文全文请访问:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42005-018-0014-7?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-Nature-Communications_Physics-Optics/Lasers-China&utm_campaign=NEWCOMMS_USG_JRCN_RL_sciencenet_nanostars_Aug_3rd
期刊介绍:Communications Physics is an open access journal from Nature Research publishing high-quality research, reviews and commentary in all areas of physics. Research papers published by the journal represent significant advances bringing new insight to a specialized area of research.
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。