论文标题:Self-implantable double-layered micro-drug-reservoirs for efficient and controlled ocular drug delivery
期刊:Nature Communications
作者:Aung Than, Chenghao Liu, Hao Chang, Phan Khanh Duong, Chui Ming Gemmy Cheung, Chenjie Xu, Xiaomeng Wang, Peng Chen
发表时间:2018/11/06
数字识别码: 10.1038/s41467-018-06981-w
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-06981-w?utm_source=other&utm_medium=other&utm_content=null&utm_
campaign=JRCN_2_RL_sciencenet_article_10.1038_s41467-018-06981-w
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lrb3h6UmoH0My7LkQO4q_A
《自然-通讯》发表的一篇论文Self-implantable double-layered micro-drug-reservoirs for efficient and controlled ocular drug delivery介绍了一种可以将药物递送至眼睛来治疗疾病的微型眼贴。该装置已在小鼠身上进行了测试,有望使患者将来能够在对家中进行眼部疾病治疗。
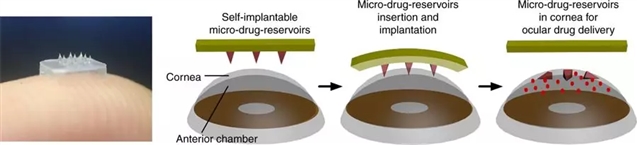
图1:接触性眼贴用于递送药物。图源:Than等
在治疗威胁视力的疾病(如青光眼和年龄相关性黄斑变性)时,许多药物直接入眼是最安全和最有效的。但是,注射可能引起不适、感染和严重眼损伤等问题,滴眼液则可能会被洗掉并且通常效率低下。
新加坡南洋理工大学的陈鹏及其同事开发了一种毫米大小的眼贴,上面包含微针阵列,这些微针以有控制的方式将药物递送至眼球。微针会逐渐溶解,缓慢地将药物释放到周围环境里面。在小鼠实验中,研究人员用拇指短暂轻压,将上述眼贴贴在小鼠眼表面。作者使用角膜新生血管作为模型,证明利用眼贴递送单克隆抗体DC101进行单次治疗后,小鼠的新生血管面积减小了约90%。相比之下,即使使用更高剂量的滴眼液,也无法取得显著的治疗效果。
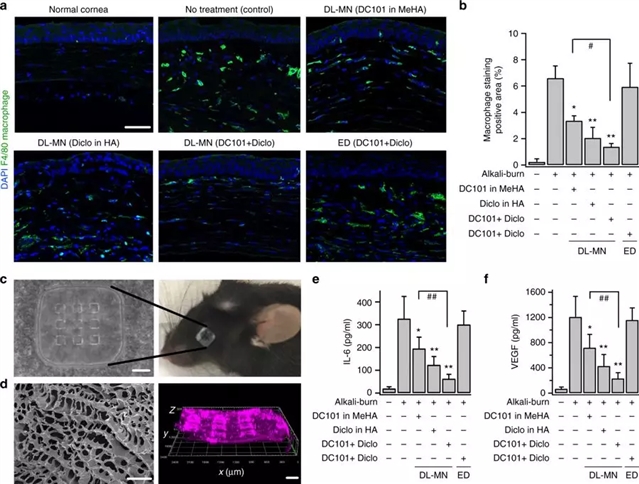
图2:使用微型贴剂组合疗法的炎症评估。 碱烧伤2天后对小鼠眼睛进行不同的治疗,并在第7天检查疗效。图源:Than等
未来,还需要开展临床研究来评估这种新装置对人类的有效性和安全性。
摘要:Eye diseases and injuries impose a significant clinical problem worldwide. Safe and effective ocular drug delivery is, however, challenging due to the presence of ocular barriers. Here we report a strategy using an eye patch equipped with an array of detachable microneedles. These microneedles can penetrate the ocular surface tissue, and serve as implanted micro-reservoirs for controlled drug delivery. The biphasic drug release kinetics enabled by the double-layered micro-reservoirs largely enhances therapeutic efficacy. Using corneal neovascularization as the disease model, we show that delivery of an anti-angiogenic monoclonal antibody (DC101) by such eye patch produces ~90% reduction of neovascular area. Furthermore, quick release of an anti-inflammatory compound (diclofenac) followed by a sustained release of DC101 provides synergistic therapeutic outcome. The eye patch application is easy and minimally invasive to ensure good patient compliance. Such intraocular drug delivery strategy promises effective home-based treatment of many eye diseases.
阅读论文全文请访问:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-06981-w?utm_source=other&utm_medium=other&utm_content=null&utm_campaign=JRCN_2_RL_sciencenet_
article_10.1038_s41467-018-06981-w
期刊介绍:Nature Communications(https://www.nature.com/ncomms/) is an open access journal that publishes high-quality research from all areas of the natural sciences. Papers published by the journal represent important advances of significance to specialists within each field.
The 2017 journal metrics for Nature Communications are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 12.353
•5-year impact factor: 13.691
•Immediacy index: 1.829
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.92656
•Article Influence Score: 5.684
•2-year Median: 8
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。