|
|
|
|
|
从DNA甲基化看草莓与番茄的不同 | Genome Biology |
|
|
论文标题:Downregulation of RdDM during strawberry fruit ripening
期刊:Genome Biology
作者:Jingfei Cheng†, Qingfeng Niu†, Bo Zhang, Kunsong Chen, Ruihua Yang, Jian-Kang Zhu, Yijing Zhang and Zhaobo Lang
发表时间:2018/12/04
数字识别码:10.1186/s13059-018-1587-x
原文链接:https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-018-1587-x?utm_source=other&utm_medium=other&utm_content=null&utm_campaign=BSCN_2_DD_GenBio_Article_Scinet
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/HSU3cmye01hUGCS52OXhbQ
中科院上海植物逆境中心郎曌博研究组在最近的一项研究中,通过整合分析不同成熟时期草莓的全基因组DNA甲基化图谱、小RNA及转录组数据,揭示了DNA甲基化在草莓果实成熟过程中的调控作用。该研究发表在Genome Biology上。

DNA甲基化是真核生物中非常保守的表观遗传修饰,它参与调控基因表达、病原菌免疫、基因印记等多种生物学过程。最近研究表明, DNA甲基化参与调控肉质果实(Fleshy fruit)的成熟。肉质果实按照其成熟过程是否发生呼吸跃变分为呼吸跃变型果实(如番茄)和非呼吸跃变型果实(如草莓)。之前的研究表明,番茄果实在成熟的过程中,由于DNA去甲基化酶SlDML2的表达上调,引起了全基因组范围内的DNA去甲基化变化,并且该变化对于果实正常成熟至关重要。但是在其他果实中,DNA甲基化是否参与调控果实成熟及其调控机制还不清楚。
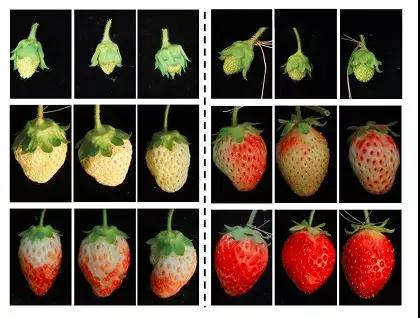
图片来自论文
中科院上海植物逆境中心郎曌博研究组此次发现,与番茄相似,草莓在成熟过程中发生基因组DNA甲基化降低现象;但同时他们的研究发现,草莓中DNA甲基化降低的分子机制与番茄中不同:番茄成熟过程中甲基化下调是由于去甲基化酶表达上调导致,而草莓中小RNA介导的DNA甲基化通路减弱则是甲基化下调的主要原因,并且成熟过程中小RNA表达下调也证实了RdDM活性的降低。该研究为定点修饰甲基化调控基因表达进而改良草莓性状提供了潜在靶点。
郎曌博:
中科院上海植物逆境生物学中心研究员/博士生导师。先后于北京师范大学和美国普渡大学获得生物学学士和植物遗传学博士学位。主要研究方向为植物中的DNA甲基化调控机制以及生物学功能。具体研究内容包括果实成熟过程中的DNA甲基化调控机制,以及与植物激素转录因子的相互作用机理。
摘要:
Background
Recently, DNA methylation was proposed to regulate fleshy fruit ripening. Fleshy fruits can be distinguished by their ripening process as climacteric fruits, such as tomatoes, or non-climacteric fruits, such as strawberries. Tomatoes undergo a global decrease in DNA methylation during ripening, due to increased expression of a DNA demethylase gene. The dynamics and biological relevance of DNA methylation during the ripening of non-climacteric fruits are unknown.
Results
Here, we generate single-base resolution maps of the DNA methylome in immature and ripe strawberry. We observe an overall loss of DNA methylation during strawberry fruit ripening. Thus, ripening-induced DNA hypomethylation occurs not only in climacteric fruit, but also in non-climacteric fruit. Application of a DNA methylation inhibitor causes an early ripening phenotype, suggesting that DNA hypomethylation is important for strawberry fruit ripening. The mechanisms underlying DNA hypomethylation during the ripening of tomato and strawberry are distinct. Unlike in tomatoes, DNA demethylase genes are not upregulated during the ripening of strawberries. Instead, genes involved in RNA-directed DNA methylation are downregulated during strawberry ripening. Further, ripening-induced DNA hypomethylation is associated with decreased siRNA levels, consistent with reduced RdDM activity. Therefore, we propose that a downregulation of RdDM contributes to DNA hypomethylation during strawberry ripening.
Conclusions
Our findings provide new insight into the DNA methylation dynamics during the ripening of non-climacteric fruit and suggest a novel function of RdDM in regulating an important process in plant development.
阅读论文全文请访问:
https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-018-1587-x?utm_source=other&utm_medium=other&utm_content=null&utm_campaign=BSCN_2_DD_GenBio_Article_Scinet
期刊介绍:
Genome Biology (https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/,13.2 - 2-year Impact Factor, 16.5 - 5-year Impact Factor) publishes outstanding research in all areas of biology and biomedicine studied from a genomic and post-genomic perspective.
The current impact factor is 13.214* and the journal is ranked 4th among research journals in the Genetics and Heredity category by Thomson Reuters. Genome Biology is the highest ranked open access journal in the category.
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。