|
|
|
|
|
SEL| 前沿研究:土壤pH驱动紫金山小海拔尺度下土壤细菌群落的分异 |
|
|
论文标题:Strong partitioning of soil bacterial community composition and co-occurrence networks along a small-scale elevational gradient on Zijin Mountain(土壤pH驱动紫金山小海拔尺度下土壤细菌群落的分异)
期刊:Soil Ecology Letters
作者:Xu Liu, Teng Yang, Yu Shi, Yichen Zhu, Mulin He,Yunke Zhao, Jonathan M. Adams, Haiyan Chu
发表时间:25 Nov 2021
DOI:10.1007/s42832-021-0122-2
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
本研究选取坐落于南京城区的紫金山,开展小海拔尺度下(300m)土壤细菌群落的微生物生物地理研究,分析了其细菌群落组成、多样性、驱动因素及共存网络特征。结果显示:紫金山土壤细菌群落沿小海拔梯度显著分异,土壤pH是其群落分异的最重要驱动力。
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Strong partitioning of soil bacterial community composition and co-occurrence networks along a small-scale elevational gradient on Zijin Mountain
Xu Liu, Teng Yang, Yu Shi, Yichen Zhu, Mulin He,Yunke Zhao, Jonathan M. Adams, Haiyan Chu
Soil Ecology Letters,
doi:10.1007/s42832-021-0122-2.
论文链接:http://journal.hep.com.cn/sel
土壤微生物具有极高的多样性,在生物地球化学循环过程调控和生态系统功能维持方面起关键作用。对土壤微生物海拔分布格局及其驱动机制的认识将有助于人们调控土壤生态功能,理解和应对气候变化和人为干扰对陆地生态系统的影响。土壤细菌群落的海拔分布,特别是大海拔尺度下的分布格局,已有广泛深入的研究。然而,小海拔尺度下的土壤细菌群落的分布模式及其驱动机制还没有得到很好的理解。
中国科学院南京土壤研究所褚海燕课题组选取坐落于南京城区的紫金山,调查了不同海拔样地的土壤细菌群落,详细研究了其群落组成、多样性、驱动因素及共存网络特征。结果表明,土壤细菌群落组成在不同海拔间显著分异(R2 = 0.12,P < 0.01)。基于距离矩阵的线性回归模型(DistLM)表明细菌群落组成与土壤pH、海拔、总氮含量和溶解性有机碳含量高度相关。其中,土壤pH是土壤细菌群落分异的最重要驱动力。此外,通过生态关联的稀疏逆协方差估计与统计推断方法(SPIEC-EASI),研究小组进一步探索了不同海拔样地中土壤细菌群落的种间共存关系,揭示了网络拓扑性质节点度和介数中心度(Degree scores和 Betweenness centralities)以及关键物种(Keystone Species)组成在不同海拔间的显著不同。上述结果表明紫金山土壤细菌群落组成和共存网络特征等沿小海拔梯度呈现出强烈分异,土壤pH是其群落变异的最重要驱动力。该项研究丰富了我们对小海拔尺度背景下土壤细菌群落的分布格局和物种共存关系的理解。
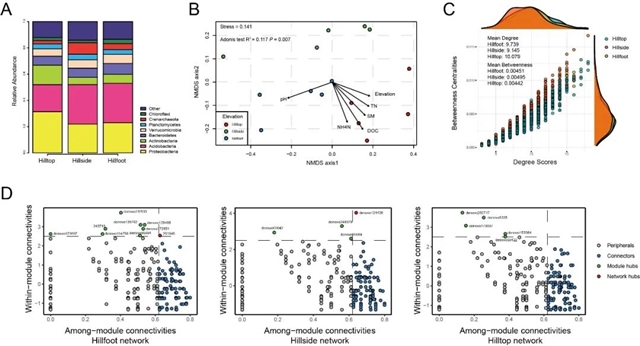
A 群落组成、B 驱动因子、C 共存网络的拓扑性质、D 关键物种
摘要
The elevational distributions of bacterial communities in natural mountain forests, especially along large elevational gradients, have been studied for many years. However, the distributional patterns that underlie variations in soil bacterial communities along small-scale elevational gradients in urban ecosystems are not yet well understood. Using Illumina MiSeq DNA sequencing, we surveyed soil bacterial communities at three elevations on Zijin Mountain in Nanjing City: the hilltop (300 m a.s.l.), the hillside (150 m a.s.l.), and the foot of the hill (0 m a.s.l.). The results showed that edaphic properties differed significantly with elevation. Bacterial community composition, rather than alpha diversity, strongly differed among the three elevations (Adonis: R2 = 0.12, P<0.01). Adonis and DistLM analyses demonstrated that bacterial community composition was highly correlated with soil pH, elevation, total nitrogen (TN), and dissolved organic carbon (DOC). The degree scores, betweenness centralities, and composition of keystone species were distinct among the elevations. These results demonstrate strong elevational partitioning in the distributions of soil bacterial communities along the gradient on Zijin Mountain. Soil pH and elevation together drove the small-scale elevational distribution of soil bacterial communities. This study broadens our understanding of distribution patterns and biotic co-occurrence associations of soil bacterial communities from large elevational gradients to short elevational gradients.
“土壤生态学”系列学术讲座
Soil Ecology Letters(SEL) 由高等教育出版社与中国科学院城市环境研究所共同主办,SpringerNature海外发行,旨在及时地反映土壤生态学研究的学术成果,报道国内外土壤生态学前沿领域的学术进展,发表文章类型主要包括Letter to editor、Perspective、Review、Rapid report、Research article、Commentary。
“土壤生态学”系列学术讲座依托中国科学院城市环境研究所、Soil Ecology Letters期刊与新媒体平台,致力于传播与分享土壤生态学前沿进展,促进土壤生态学科研工作者的交流。
期刊定位
SEL(Soil Ecology Letters) 2019年正式创刊。定位为土壤生态学领域类高水平科技期刊。旨在全球范围内充分、及时、全面地反映土壤生态学领域研究进展,报道国内外土壤生态学前沿领域高水平的学术成果。
报道领域
报道领域包括:土壤生物多样性、土壤互营和食物网、土壤微生物组、土壤—植物相互作用、土壤生物地球化学循环、土壤生物修复和恢复、土壤多功能性、土壤生物对环境变化的响应和适应、土壤生态过程的突破性技术、新理论和模型。
期刊栏目
期刊栏目包括:letter to editor, perspective, review, rapid report, research article, commentary。栏目不限于此,还可以有Image、News等。
论文绿色通道:SEL优先快速发表高质量论文。
出版模式
快速出版:加速审稿,一经录用,即以Just accepted形式发布。定稿后online在线发布。
出版费用:免一切费用,包括审稿费、彩图费、出版印刷费等。
收 录
ESCI, SCOPUS, BIOSIS, Biological Abstracts, Google Scholar等。
国内全文免费获取
联系方式
期刊主页:
http://journal.hep.com.cn/sel
https://link.springer.com/journal/42832
投稿网址:
https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/selett
编辑部:
电话:0592-6190560;010-58556534
邮箱:SEL@iue.ac.cn;SEL@pub.hep.cn

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、
、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
高等教育出版社入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划”集群化项目。Frontier系列期刊中:13种被SCI收录;1种被A&HCI收录;6种被Ei收录;2种被MEDLINE收录;11种中国科技核心期刊;16种被CSCD收录。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。