|
|
|
|
|
增塑剂被蔬菜吸收了吗?| Food Production,Processing and Nutrition |
|
|
论文标题:Uptake and accumulation of di-n-butyl phthalate in six leafy vegetables under hydroponic conditions
期刊:Food Production,Processing and Nutrition
作者:Yong Li, Huang-qian Yan et.al
发表时间:2019/11/26
数字识别码:10.1186/s43014-019-0009-0
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)被广泛应用于工业和家用产品,如一般塑料制品、塑料薄膜、玩具、个人护理用品、食品包装和医疗产品等。含PAE产品的广泛使用导致PAE频繁出现在水源、土壤、空气、食物甚至是生物系中。那么,该类物质会被种植的蔬菜吸收么?
来自江苏省农业科学院余向阳研究员课题组的一项研究对比了6种叶菜在水培条件下对邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)的吸收和积累,该研究在线发表在Food Production,Processing and Nutrition上。
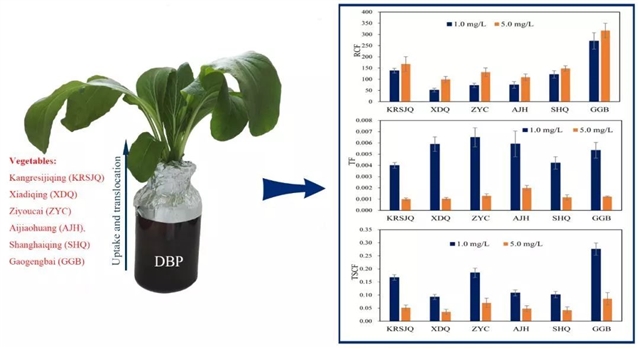
图1
邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)又称酞酸酯,主要用于聚氯乙烯材料,可使聚氯乙烯由硬塑胶变为有弹性的塑胶,起到增塑剂的作用,已广泛用于塑料制品中。塑料制品中的PAEs通过氢键和范德华力与塑料分子连接,因此,塑料的使用致使PAEs不断地被释放到外界环境中,造成严重的环境污染。同时,在各类日化用品、食品包装及医疗产品中我们可能接触到PAEs,这一环境内分泌干扰物会对人体健康有严重的危害。
邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)是PAEs中的一种,已成为一种环境中普遍存在的污染物。本研究通过水培试验研究6种叶菜类蔬菜(抗热四季青、夏帝青、紫油菜、矮脚黄、上海青和高梗白)对DBP的吸收和累积的规律。结果发现,6种蔬菜均可以从水中吸收DBP并向茎叶中转移,而根中DBP浓度远大于茎叶中的浓度,说明DBP易在蔬菜根部富集,不易向茎叶中转移。

抗热四季青 夏帝 青紫油菜

矮脚黄 上海青 高梗白
另外,不同蔬菜对DBP的吸收和累积能力存在一定差异,其中,高梗白、抗热四季青、上海青的根部对DBP累积能力比较强,而夏帝青、紫油菜、矮脚黄的茎叶部分对DBP累积能力比较强,研究结果将为农产品质量安全生产以及低塑化剂积累品种筛选提供依据。
本文的研究得到了江苏省自然科学基金的支持。
本研究的第一作者为李勇博士,现任江苏省农业科学院农产品质量安全与营养研究所副研究员,主要从事农产品营养品质安全及代谢组学技术研究,主持国家自然科学基金、江苏省自然科学基金、江苏省农业科技自主创新资金等项目,以第一作者在发表论文12篇,其中SCI论文10篇。

图4:余向阳研究员
本研究的通讯作者为余向阳研究员,长期从事农产品产地环境污染物残留检测、风险评估及危害消减技术等方面研究工作。现任江苏省农业科学院科研管理处处长、农产品质量安全与营养研究所产地环境研究室主任、农业部农产品质量安全风险评估实验室岗位专家、国家桃产业技术体系质量安全与营养品质评价岗位科学家、中国植物保护学会青年委员会副主任。获江苏省科技进步二等奖2项、三等奖1项、江苏省农业技术推广奖二等奖1项,以及江苏省“333”高层次人才培养工程第三层次培养对象、江苏省“六大人才高峰”高层次人才培养对象、江苏省优秀中青年科学技术带头人等荣誉称号。近五年,主持国家自然科学基金、江苏省重点研发计划、江苏省农业科技自主创新资金等省部级以上项目10余项,发表论文46篇,其中SCI论文24篇,授权发明专利和国际专利20余项,主编著作1部,参与制定行业和地方标准10余项。

图5
The Food Production, Processing and Nutrition journal aims to provide a unique dedicated forum for publication of the highest quality and novel contributions in the field. Both fundamental research and applied areas are of interest and these extend to food production with respect to variety improvement and selection as well as green processing. Food safety, elimination of contaminants, and retention of nutrients and bioactive components that play a role in health promotion of consumers, are important aspects that will be covered. Production technologies, absorption, bioavailability and personalized nutrition with consideration of gut microbiota are also of interest to the journal. Results may be communicated in the form of original research, reviews.
摘要:The uptake and accumulation of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) in six leafy vegetables was investigated under hydroponic conditions. The test vegetables were six varieties of Brassica campestris ssp., including Kangresijiqing (KRSJQ), Xiadiqing (XDQ), Ziyoucai (ZYC), Aijiaohuang (AJH), Shanghaiqing (SHQ) and Gaogengbai (GGB). The root concentration factor (RCF), translocation factor (TF) and transpiration stream concentration factor (TSCF) were calculated in order to compare the difference of uptake and accumulation behaviours of DBP in vegetable varieties. The results showed that DBP was easily concentrated in vegetable roots, but was poorly translocated from the roots to the shoots. Among the six vegetables, the ability of concentrating DBP from the solution to shoots was the highest in GGB, followed by ZYC, KRSJQ, AJH, SHQ and XDQ. High concentrations of DBP (5.0 mg/L) seem to inhibit normal physiological activity in the vegetables, which resulted in a higher RCF and a lower TF and TSCF than in low-concentration treatment. The results will help to evaluate the safety of agricultural products and to provide evidence for screening DBP pollution-safe vegetable cultivars.
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。