|
|
| 血液处理和白细胞分离方法影响免疫细胞的整体转录组 | BMC Immunology |
|
论文标题:Blood handling and leukocyte isolation methods impact the global transcriptome of immune cells
期刊:BMC Immunology
作者:Brittany A. Goods, Jacqueline M. Vahey†, Arthur S. Steinschneider†, Michael H. Askenase, Lauren Sansing† and J. Christopher Love
发表时间:2018/10/30
数字识别码:10.1186/s12865-018-0268-6
原文链接:https://bmcimmunol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12865-018-0268-6?utm_source=other&utm_medium=other&utm_content=null&utm_campaign=BSCN_2_DD_Sciencenet_Article
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rold8a5fl3QSI7w8InXuPQ
转录谱分析可以为组织和疾病的细胞状态和表型提供宝贵的信息。这种方法特别适用于在例如药物或疾病状态等干扰情况下对细胞和组织进行研究,所得到的数据有助于推测感兴趣的目标通路、独特的功能状态、与疾病状态的相关性以及新的亚型分类。
某些测序方法,例如Smart-Seq2,能够利用从极少量细胞(大约1-1000)中提取的RNA来测定转录组,因此能够分析细胞数目极低、细胞类型罕见或依赖于生物标记材料的临床样本。许多研究已经确定了低输入或降解RNA样本的最佳处理程序和分析方法。全血防腐剂和稳定剂的使用也使得利用极少量血获取高质量数据成为可能。然而,将转录组分析应用到临床样本(如组织和已分类的细胞群)在样本采集、样本处理和组织分离方面遇到了独特而重大的挑战。例如,多中心研究常常需要对患者样本进行集中处理,这种转移有引入偏倚的风险。此外,RNA质量在组织之间可能存在很大差异,这或许会影响实验设计。对于稀少或难以处理的样品而言,仅靠获取足够的高质量样品并不总能实现高RNA质量目标队列的规模要求。
以往的研究很少关注RNA测序过程中由于样本处理而引入转录组数据的人为因素。对于微阵列或定量PCR产生的表达谱,已有研究发现一些能够影响结果数据的因素。其中一项研究表明,标准白细胞采集程序之前的培养时间可以迅速改变血液的转录组。在4°C进行运输可能会减轻这些变化,但无法完全消除影响。另一个研究利用微阵列技术探寻了时间、温度和保存对分离外周血单核细胞(PBMCs)转录组的影响:每一种保存材料都对转录组有影响,但依赖于大量的血液。到目前为止,只有少数的研究阐明了通过白细胞分离方法和低输入RNA测序所引入的人为影响因素。
在这篇文章中,研究人员描述了血液处理、白细胞分离方法和血液中分离得到的少量免疫细胞的保存方法对转录组的整体影响。他们发现,在白细胞分离和分类之前,血液的储存/运输温度会导致CD8+ T细胞和单核细胞的整体变化,包括免疫相关基因的改变。通过使用白细胞过滤系统,这些变化可以被最小化。研究人员使用这种方法从来自急性脑出血患者血液的免疫细胞中获得了高质量的转录组数据,并与健康对照组相匹配。这些数据证明了这种过滤方法的实用性,并强调了在进行转录组分析之前,必须使用明确的、紧密匹配的方法来处理样本。
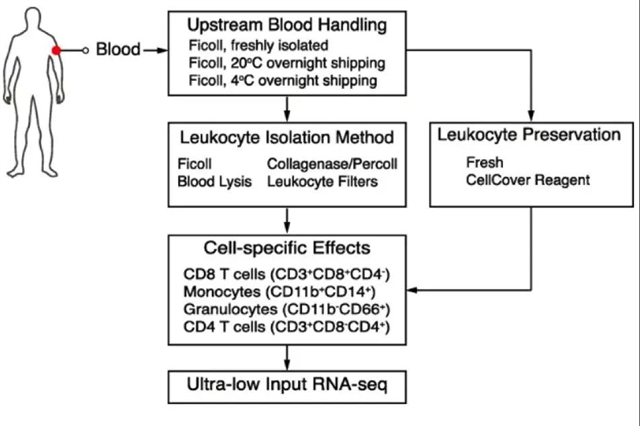
图1. 样品处理方法模式图。本图描述了临床免疫学中用到的不同样品处理方法,图中包括血液运输温度(20°C或4°C),外周血单核细胞分离方法(Ficoll梯度、卡拉胶酶加Percoll梯度、全血溶解、白细胞过滤),以及所研究的不同类型的免疫细胞(CD8+ T细胞、CD4+ T细胞、粒细胞或单核细胞)。
本研究的结果强调了在转录组研究中使用明确的可比较的方法十分必要,同时提出了一种能够用于快速分离目的免疫细胞并使得转录组分析偏倚最小化的过滤方法。
摘要:
Background
Transcriptional profiling with ultra-low input methods can yield valuable insights into disease, particularly when applied to the study of immune cells using RNA-sequencing. The advent of these methods has allowed for their use in profiling cells collected in clinical trials and other studies that involve the coordination of human-derived material. To date, few studies have sought to quantify what effects that collection and handling of this material can have on resulting data.
Results
We characterized the global effects of blood handling, methods for leukocyte isolation, and preservation media on low numbers of immune cells isolated from blood. We found overall that storage/shipping temperature of blood prior to leukocyte isolation and sorting led to global changes in both CD8+ T cells and monocytes, including alterations in immune-related gene sets. We found that the use of a leukocyte filtration system minimized these alterations and we applied this method to generate high-quality transcriptional data from sorted immune cells isolated from the blood of intracerebral hemorrhage patients and matched healthy controls.
Conclusions
Our data underscore the necessity of processing samples with comparably defined protocols prior to transcriptional profiling and demonstrate that a filtration method can be applied to quickly isolate immune cells of interest while minimizing transcriptional bias.
阅读论文全文请访问:
https://bmcimmunol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12865-018-0268-6?utm_source=other&utm_medium=other&utm_content=null&utm_campaign=BSCN_2_DD_Sciencenet_Article
期刊介绍:
BMC Immunology(https://bmcimmunol.biomedcentral.com/, 2.615 -2-year Impact Factor, 2.646 -5-year Impact Factor) is an open access journal publishing original peer-reviewed research articles in molecular, cellular, tissue-level, organismal, functional, and developmental aspects of the immune system as well as clinical studies and animal models of human diseases.
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。