|
|
| FESE | 前沿研究:以最小的成本实现大气污染减排目标:一种兼有公平性和可行性约束的企业级分配方法 |
|
论文标题:Achieving air pollutant emission reduction targets with minimum abatement costs: An enterprise-level allocation method with constraints of fairness and feasibility(以最小的成本实现大气污染减排目标:一种兼有公平性和可行性约束的企业级分配方法)
期刊:Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering
作者:Yanfei Chen, Ji Zheng, Miao Chang, Qing Chen, Cuicui Xiao
发表时间:15 Feb 2022
DOI:10.1007/s11783-021-1459-6
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章

原文链接(点击“阅读原文”直接获取)
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fese/EN/10.1007/s11783-021-1459-6
文章出版:Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16(2): 25
原文信息
题目:
Achieving air pollutant emission reduction targets with minimum abatement costs: An enterprise-level allocation method with constraints of fairness and feasibility
作者:
Yanfei Chen1, Ji Zheng1, Miao Chang ( )1, Qing Chen(
)1, Qing Chen( )1, Cuicui Xiao2
)1, Cuicui Xiao2
作者单位:
1 Tsinghua University, China2 University of Science and Technology Beijing, China
通讯作者邮箱:
changmiao@tsinghua.edu.cn
qchenthuruc@163. com
关键词:
Pollutant emission reduction allocation (污染物减排分配);
Emission reduction measures (减排措施);
Total abatement cost (减排总成本);
Economic efficiency (经济效益);
Abatement space (减排空间)
文章亮点
• 对污染物减排分配的效率和公平性进行了优化;
• 将分配结果进一步细化到企业的不同减排措施中;
• 优化后的分配结果降低了减排成本,挖掘了减排空间;
• 为不同减排配额的企业提供了减排建议。
文章简介
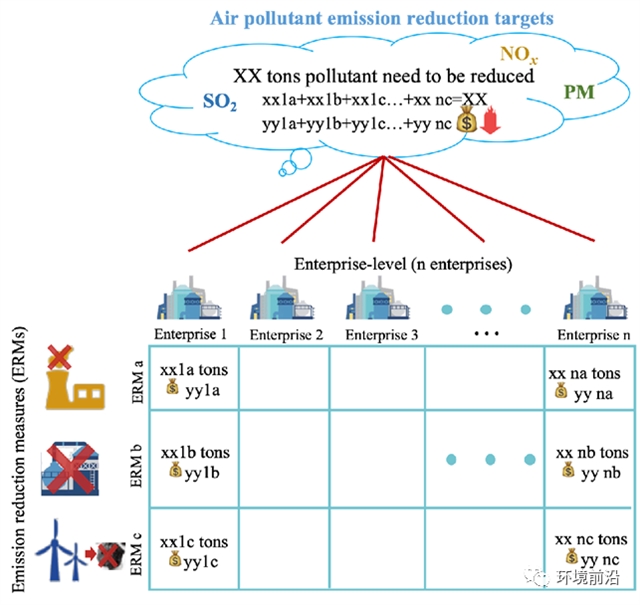
为实现大气污染物的减排目标,中国正在不断推进污染物的总量控制。然而,传统的污染物减排分配模式忽视了经济成本,往往导致减排途径不合理。作为减排的主体,工业企业不得不花费高昂的成本。因此,本研究以经济效益作为主要考虑因素,以工业企业的具体减排措施(ERMs)为最小分配单元,以总减排成本(TAC)最小化为目标函数,以公平性和可行性作为减排分配的约束条件,构建了一个企业级污染物减排分配(EPERA)模型。以中国的M市为例,利用EPERA模型构建了帕累托(Pareto)最优边界,并得到了最佳权衡的结果。结果表明,在基本和严格两种减排规定下,与只考虑公平性时相比,最佳权衡点的TAC分别减少了46.40%和45.77%,基尼系数分别为0.26和0.31。在成本可控、分配相对公平合理的情况下,实现了减排目标。此外,在不同ERMs下分配到不同减排配额的企业有自身的特点,需要针对性地优化技术和设备,使企业在相同的减排成本下达到最佳的减排效果。
文章摘要图
编委点评
污染物总量控制对改善空气质量发挥了重要作用,合理分配污染物减排量是保障制度实施的关键,并且经济效率与公平性二者的平衡至关重要。本研究重点考虑经济效率,同时考虑公平性和可行性,建立了企业级污染物减排分配模型,并进行了应用。该研究从企业级污染物减排配置的层面,为环境和经济协调发展提供了新的视角和方法。
编者 | 王帅
点评 | 张宏亮
致 谢
张宏亮,男,复旦大学环境科学与工程系教授,FESE青年编委。研究方向为大气污染模型的开发及其在污染物形成、溯源、健康和气候效应方面的运用。个人主页:
https://environment.fudan.edu.cn/5b/8e/c26241a351118/page.htm
王帅,男,复旦大学环境科学与工程系2020级环境科学专业直博生,导师为张宏亮教授,研究方向为高分辨大气污染数据集构建及应用。
摘要
For achieving air pollutant emission reduction targets, total pollutant amount control is being continuously promoted in China. However, the traditional pattern of pollutant emission reduction allocation regardless of economic cost often results in unreasonable emission reduction pathways, and industrial enterprises as the main implementers have to pay excessively high costs. Therefore, this study adopted economic efficiency as its main consideration, used specific emission reduction measures (ERMs) of industrial enterprises as minimum allocation units, and constructed an enterprise-level pollutant emission reduction allocation (EPERA) model with minimization of the total abatement cost (TAC) as the objective function, and fairness and feasibility as constraints for emission reduction allocation. Taking City M in China as an example, the EPERA model was used to construct a Pareto optimal frontier and obtain the optimal trade-off result. Results showed that under basic and strict emission reduction regulations, the TAC of the optimal trade-off point was reduced by 46.40% and 45.77%, respectively, in comparison with that achieved when only considering fairness, and the Gini coefficient was 0.26 and 0.31, respectively. The abatement target was attained with controllable cost and relatively fair and reasonable allocation. In addition, enterprises allocated different emission reduction quotas under different ERMs had specific characteristics that required targeted optimization of technology and equipment to enable them to achieve optimal emission reduction effects for the same abatement cost.
期刊简介

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、 、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。