论文标题:Reducing Threats From Contamination and Flood Damage: Restoring the Brandywine Creek Edge in Wilmington, Delaware, USA(降低污染和洪水威胁:以美国特拉华州威尔明顿市布兰迪万溪周边环境修复为例)
期刊:Landscape Architecture Frontiers
作者:Galen NEWMAN, CAI Zhenhang, Jennifer HORNEY, LYU Wuqi
发表时间:14 Sep 2022
DOI:10.15302/J-LAF-1-040030
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章


论文信息
DOI: 10.15302/J-LAF-1-040030
降低污染和洪水威胁:以美国特拉华州威尔明顿市布兰迪万溪周边环境修复为例
盖伦·纽曼1,蔡镇航1,詹妮弗·霍尼2,吕吴琦1
1 美国德克萨斯农工大学景观建筑和城市规划系
2 美国特拉华大学灾害研究中心
摘要
近年来,人们愈发关注公共卫生,以及因洪水灾害和环境污染而产生的有毒物质的迁移与转化问题。设计规划人员也一直在努力探索能够有效应对此类问题的解决方案,期望通过合适的定量方法评估相关方案的影响。
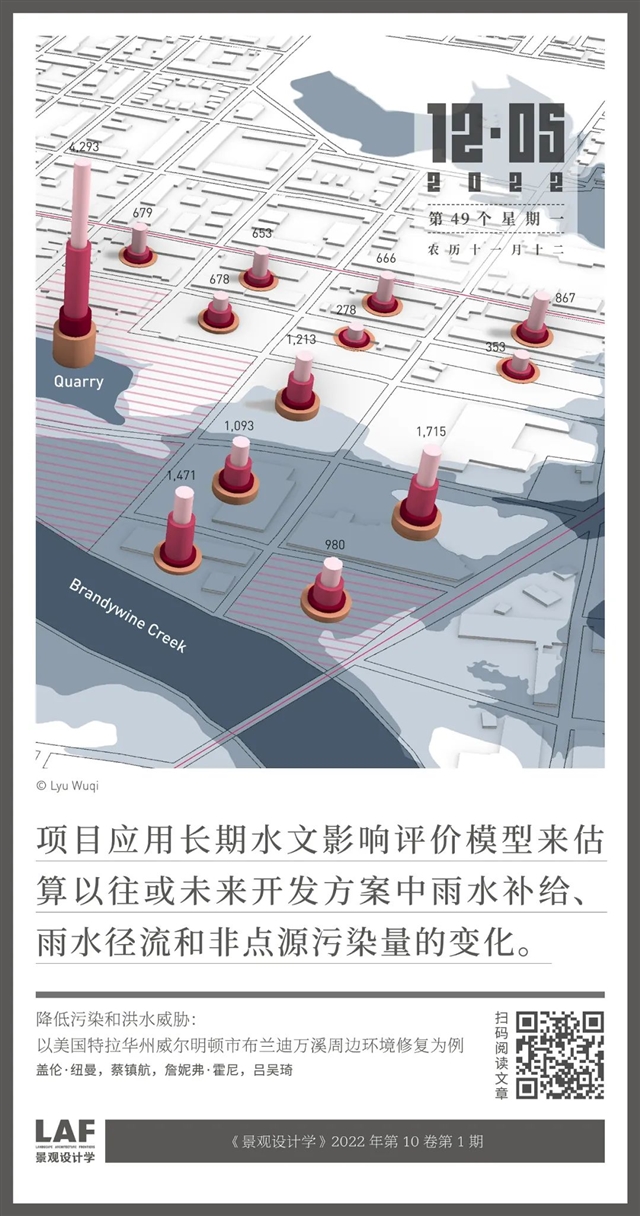
本文以美国威明顿市布兰迪万溪周边一处面积约为52.6hm2的场地为例,识别了场地所在街区当前面临的问题和需求:自20世纪中叶以来,场地经历了高度的工业化发展,除洪水威胁外,附近工业用地、棕地及合流污水管道中的污染物也会随洪水迁移至场地中,极大影响了人们的健康和生活质量。鉴于此,项目团队开发了一套分阶段实施的总体规划方案,以期减少雨洪径流并去除污染物,同时将场地中现有的棕地改造为环境优美的绿地,鼓励更具韧性的场地开发举措。
项目应用长期水文影响评价(L-THIA)模型来衡量设计方案的影响和绩效。结果显示,相较土地利用现状,本项目提出的总体规划方案能够更有效地减少雨水径流和污染负荷——雨水径流将减少约24.35%,污染物去除量将增加38.08%。
关键词
绿色基础设施;景观绩效;洪水韧性;污染;暴雨;L-THIA模型;方案评估
Reducing Threats From Contamination and Flood Damage: Restoring the Brandywine Creek Edge in Wilmington, Delaware, USA
Galen NEWMAN1, CAI Zhenhang1,
Jennifer HORNEY2, LYU Wuqi1
1 Department of Landscape Architecture and Urban Planning, Texas A&M University, USA
2 Disaster Research Center, University of Delaware, USA
Keywords
GreenInfrastructure;LandscapePerformance;FloodResilience;Contamination;Stormwater;
L-THIA; Master Plan Assessment
摘要
Located in Wilmington, Delaware, along the shoreline of the Brandywine Creek in the Greater Philadelphia/Delaware River Watershed, this project responds to a specific and critical need for the site as prioritized by multiple stakeholders. The project applies an innovative approach for quantifying increased flood resilience while simultaneously reducing contamination levels through the implementation of green infrastructure. To solve joint issues related to increased flood risk concurrent with higher potential for exposure to environmental contaminants transported in flood waters from adjacent industrial sites, brownfields, and combined sewer overflows, the research team develops a phased approach to decreasing stormwater runoff and pollutant loads on a 130-acre (52.6 hm2) site along the Brandywine Creek, applying the Long-Term Hydrologic Impact Assessment (L-THIA) model to quantify design impacts and performance of a master plan. Overall, the proposed master plan can reduce stormwater runoff and pollutant loads to levels significantly less than existing conditions or the current land use plan. Further, this research is unique in that it uses outputs from the L-THIA to compare existing conditions, effects of the current comprehensive plan, and impacts related to the proposed neighborhood-scaled master plan to evaluate the effectiveness between each scenario.
编辑 | 王颖 田乐
注:本文由作者及来源机构授权景观设计学前沿发布,未经授权不得以任何形式、任何文种在其他印刷版、网络版等媒介发表,如有违反,本刊将保留追究其法律责任的权利。若有转载,请后台回复关键词“转载”联系授权。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、 、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
高等教育出版社入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划”集群化项目。Frontier系列期刊中:13种被SCI收录;1种被A&HCI收录;6种被Ei收录;2种被MEDLINE收录;11种中国科技核心期刊;16种被CSCD收录。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。