中山大学曹楠团队发现,鞘脂代谢控制哺乳动物心脏再生。这一研究成果于2024年2月16日在线发表在国际学术期刊《细胞—代谢》上。
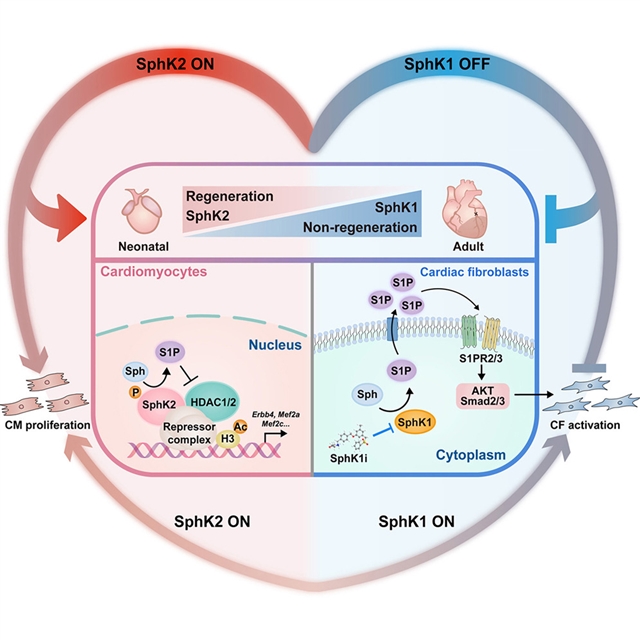
研究人员展示了新生儿心脏损伤后广泛的鞘脂代谢重塑,并发现产生相同鞘脂代谢物鞘磷脂-1-磷酸(S1P)的同工酶SphK1和SphK2对心脏再生的调节作用不同。SphK2在心脏发育过程中下调,并通过核S1P依赖性调节组蛋白乙酰化来决定心肌细胞(CM)的增殖。重新激活SphK2可诱导成体CM细胞周期再入和细胞分裂,从而促进再生。
相反,SphK1在发育过程中上调,并通过S1P自分泌机制促进心脏成纤维细胞纤维化。通过微调每种SphK同工酶的活性,研究人员开发出了一种疗法,它能同时促进心肌修复和限制纤维化瘢痕,从而使梗死的成年心脏再生。
据介绍,哺乳动物出生后利用脂质作为能量底物会导致CM细胞周期停滞并丧失再生能力。除了提供能量,适当管理脂质成分对细胞和生物体的健康至关重要,但其在心脏再生中的作用仍不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Sphingolipid metabolism controls mammalian heart regeneration
Author: Xiaoqian Ji, Zihao Chen, Qiyuan Wang, Bin Li, Yan Wei, Yun Li, Jianqing Lin, Weisheng Cheng, Yijie Guo, Shilin Wu, Longkun Mao, Yuzhou Xiang, Tian Lan, Shanshan Gu, Meng Wei, Joe Z. Zhang, Lan Jiang, Jia Wang, Jin Xu, Nan Cao
Issue&Volume: 2024-02-16
Abstract: Utilization of lipids as energy substrates after birth causes cardiomyocyte (CM) cell-cyclearrest and loss of regenerative capacity in mammalian hearts. Beyond energy provision,proper management of lipid composition is crucial for cellular and organismal health,but its role in heart regeneration remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate widespreadsphingolipid metabolism remodeling in neonatal hearts after injury and find that SphK1and SphK2, isoenzymes producing the same sphingolipid metabolite sphingosine-1-phosphate(S1P), differently regulate cardiac regeneration. SphK2 is downregulated during heartdevelopment and determines CM proliferation via nuclear S1P-dependent modulation ofhistone acetylation. Reactivation of SphK2 induces adult CM cell-cycle re-entry andcytokinesis, thereby enhancing regeneration. Conversely, SphK1 is upregulated duringdevelopment and promotes fibrosis through an S1P autocrine mechanism in cardiac fibroblasts.By fine-tuning the activity of each SphK isoform, we develop a therapy that simultaneouslypromotes myocardial repair and restricts fibrotic scarring to regenerate the infarctedadult hearts.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.01.017
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(24)00017-2
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
