|
|
|
|
|
FoAR 社区环境在儿童活跃的学校通勤、独立出行以及体能活动中的作用 |
|
|
论文标题:Understanding children’s active school commute, independent mobility, and physical activity in Austin, Texas, USA: Roles of physical environments
期刊:Frontiers of Architectural Research
作者:Xuemei Zhu, Lingyi Qiu, Hanwool Lee, Chanam Lee
发表时间:15 Oct 2024
DOI: 10.1016/j.foar.2024.02.016
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章

FoAR是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 A&HCI / CSCD / Scopus / DOAJ / CSTPCD 收录

01
论 文 题 目
Manuscript Title
Understanding childrens active school commute, independent mobility, and physical activity in Austin, Texas, USA: Roles of physical environments
社区环境在儿童活跃的学校通勤、独立出行以及体能活动中的作用
02
作 者
Authors
Xuemei Zhu (a)*, Lingyi Qiu (b), Hanwool Lee (c), Chanam Lee (c)
(a) Department of Architecture, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA
(b) Huckabee College of Architecture, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, USA
(c) Department of Landscape Architecture & Urban Planning, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA
03
论 文 摘 要
Abstract
Walking to/from school (WTS) is an important form of habitual and healthful physical activity (PA). This cross-sectional study examined the multilevel correlates of WTS among elementary school children in Austin, Texas, and whether WTS and neighborhood environmental factors were associated with increased independent mobility and PA. A parent survey was conducted, and geographic information systems were used to calculate the shortest home-to-school distance. Binary logistic regressions were used to predict the outcomes. Distance, physical barriers (e.g., highway/freeway/busy roads), neighborhood environmental quality, and traffic concerns were significant predictors for WTS. Having a school within the neighborhood and unsupervised play increased the likelihood of independent travel to non-school destinations. Sidewalk availability and condition, having a friend’s/relative’s house in the neighborhood that the child visits frequently, and independent travel to non-school destinations predicted an increased likelihood of unsupervised outdoor play. Stranger danger reduced the likelihood of both independent travel and unsupervised play. Easy access to services and unsupervised play increased the likelihood of meeting PA guidelines. This study identified modifiable environmental predictors of WTS, independent mobility, and meeting PA guidelines. Future PA promotion should consider strategies that can encourage not only WTS but also independent travel to non-school destinations and unsupervised outdoor play.
步行上下学(WTS)是一种重要的习惯性健康体能活动(PA)。这项横断面研究考察了与美国德克萨斯州奥斯汀市小学生步行上下学相关的多层次因素,以及步行上下学、社区环境是否与独立出行及体能活动的增加有关。该研究通过对学生家长进行问卷调查收集数据,使用地理信息系统计算家到学校的最短距离,并采用二元逻辑回归模型进行分析。路程距离、社区障碍(例如高速公路、城市快速路、繁忙街道)、社区环境质量和交通问题都是步行上下学的重要预测因素。社区内设的学校以及无人看护的玩耍都可以增加孩子们独立前往学校之外目的地的可能性。人行道的可用性与状态、社区内有朋友或亲戚家,以及前往学校之外目的地的独立行程,都预示着孩子在无人看护的情况下在户外玩耍的可能性的增加。孩子对陌生人的恐惧会降低其独立出行以及无人看护情况下玩耍的可能性。便利的服务设施以及无看护玩耍也增加了实现体能活动标准的可能性。本研究明确了步行上下学、独立出行以及完成体能活动标准的环境预测因素。为了今后进一步提高孩子的体能活动水平,我们不仅需要提倡他们步行上下学,还应鼓励他们独立出行前往学校以外的目的地,以及在无人看护的情况下安全地进行其它活动。
04
关 键 词
Keywords
Walking to school / 步行上下学
Independent mobility / 独立出行
Play / 玩耍
Physical activity / 体能活动
Neighborhood environment/ 社区环境
Children / 儿童
05
章 节 标 题
Sections Title
1. Introduction / 引言
1.1. Background / 研究背景
1.2. Study aims / 研究目的
2. Materials and methods / 研究内容及方法
2.1. Study design, study settings, and population / 研究设计、环境、人群
2.2. Data collection and analysis / 数据收集与分析
3. Results / 研究成果
3.1. Survey responses and descriptive statistics of the outcome variables / 调查反馈以及结果变量的描述性统计数据
3.2. Research Question 1: what physical environmental factors predicted WTS? / 研究问题 1:哪些社区环境因素可预测步行上下学的意向?
3.3. Research Question 2: do WTS and neighborhood physical environmental factors predict independent travel to non-school destinations (Question 2a), unsupervised outdoor play (Question 2b), and meeting PA guidelines (Question 2c)? / 研究问题 2:步行上下学以及社区环境因素是否能够预测前往学校以外目的地的独立出行(问题 2a)、无人看护情况下的户外玩耍(问题 2b)以及是否符合体能活动(PA)的标准要求(问题 2c)?
4. Discussion / 讨论
4.1. Study limitations / 研究的局限性
4.2. Key findings and implications for future research and practice / 对未来研究与实践的关键性发现和影响
5. Conclusions / 结论
06
主 要 插 图
Illustrations
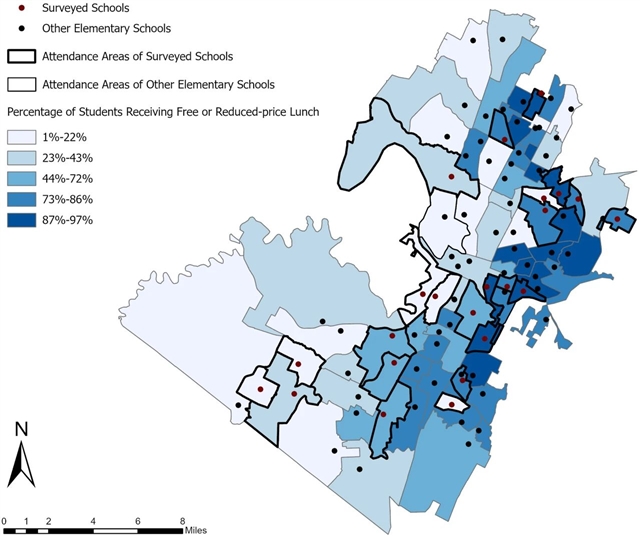
▲ 图一:奥斯汀独立学区(AISD)内各所学校所在的位置以及有资格享受免费或减价午餐的学童所占的百分比。
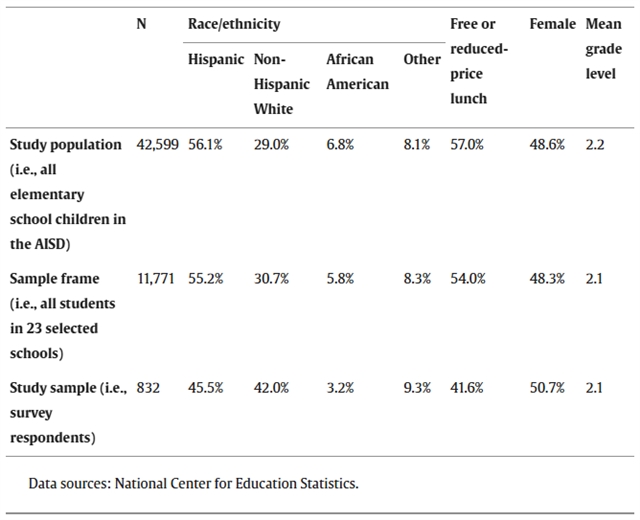
▲ 表一:研究人群、样本框架以及研究样本的社会人口学特征。

▲ 表二:结果变量的描述性统计数据。
07
作 者 介 绍
Authors’ Information

Xuemei Zhu
Professor
Department of Architecture
Texas A&M University, College Station, USA
Dr. Xuemei Zhu is a Professor in the Department of Architecture and a Faculty Fellow in the Center for Health Systems & Design at Texas A&M University. She is also a Presidential Impact Fellow and the holder of the Ronald L. Skaggs, FAIA & Joseph Sprague, FAIA Chair in Health Facilities Design, and the Co-director of the research group on Design Research for Active Living. Dr. Zhu’s scholarship investigates the impacts of the built environment on public health and social equity, with a specific focus on active living, healthy communities, evidence-based healthcare design, school design, and workplace design, using interdisciplinary approaches. Her research is supported by agencies such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), and the American Institute of Architects (AIA), with a total support of about $7.3 million. She has published extensively in the fields of environmental design and planning, environment-behavior research, and public health. Her teaching centers on the theme of environment-behavior relationships and strengthens the link between environment-behavior research and design practice.

Lingyi Qiu
Assistant Professor
Huckabee College of Architecture
Texas Tech University, Lubbock, USA
Dr. Lingyi Qiu is an Assistant Professor in the Huckabee College of Architecture at Texas Tech University. She received her doctorate in Architecture and the Certificate in Health Systems & Design from Texas A&M University and is certified in Evidence-Based Design Accreditation and Certification (EDAC). Her research focuses on healthy housing and communities, healthy buildings, active living research, and environment-behavior research. One of her studies, Impacts of Housing and Neighborhood Environments on Childrens Independent Mobility, addresses an important yet understudied topic: the roles of housing and neighborhood environments in supporting elementary school childrens home-based independent mobility, while also accounting for personal and social factors.

Hanwool Lee
Post-doctoral Research Associate
Department of Landscape Architecture & Urban Planning
Texas A&M University, College Station, USA
Dr. Hanwool Lee is a post-doctoral research associate at Texas A&M University. His major is urban planning and design. He is interested in measuring/quantifying urban form and other elements of urban environments and their impact on pedestrian behavior. He is especially an expert in the handling of GIS data.

Chanam Lee
Professor / Executive Associate Dean
Department of Landscape Architecture & Urban Planning
Texas A&M University, College Station, USA
Chanam Lee is a Professor of Landscape Architecture and Urban Planning and founding director of Design Research for Active Living (DrAL), at Texas A&M University. Lees research focuses on linking the built environment with public health outcomes. Her expertise is in active living research,’ a transdisciplinary area of research that deals with environmental and policy approaches toward promoting physical activity. Lees contributions to this relatively new area of scholarship is significant in: (a) developing methodological and theoretical foundations, (b) bringing attention to high-risk populations, and (c) translating research into tools/guides to facilitate evidence-based policy/design interventions. Lee has led 25 externally funded projects as the PI or Co-PI at TAMU, funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, National Institute of Health, etc., totaling almost $15 million. Two of her on-going NIH R01 projects, titled Active Living Austin and Active El Paso, exemplify her current and continued focus on advancing environment-health research by establishing causality and addressing disparity. Lee (co)authored over 100 peer-reviewed publications in leading journals/books in health and design/planning disciplines, and is among the most cited scholars in her field. She has made almost 300 presentations including 150 conference and 60 invited keynote/plenary presentations. She is the recipient of the Excellence in Research and/or Creative Works Award, Senior Level, in 2020 from the Council of Educators in Landscape Architecture. The significance of her scholarship has been recognized by multiple other awards from American Public Health Association, American Society of Landscape Architects, Scott & White Healthcare, and Center for Transportation Studies. Her work has also impacted professional practices in urban planning and landscape architecture, by informing new policy development and by providing evidence-based guides for multiple built and under-construction design projects in the U.S., Japan and Nigeria. These projects range from hospital healing garden designs to large-scale health-oriented community planning projects.
08
原 文 阅 读
Download Link

长按上方二维码|浏览本期精彩论文
▼ 点击下方词条 | 往期精彩不容错过
#期刊快讯#系列
1/ 主编王建国院士团队荣获国家科技进步奖一等奖
2/ FoAR|2021年度报告,2022新年快乐!
3/ FoAR|2022年度报告,2023新年快乐!
4/ FoAR|2023年度报告,2024新年快乐!
5/ 最新|FoAR 2023 CiteScore 指数上升为6.2
6/ JCR最新|FoAR 2023年度影响因子3.1,两项评价指标均位列WoS核心合集建筑类第一
7/ 最新|FoAR 被中国科技论文与引文数据库(CSTPCD)收录
8/ 最新|FoAR 再次入选中国国际影响力优秀学术期刊
9/ 最新|FoAR 荣获科爱十大优秀期刊奖
10/ 最新|FoAR进入2023年中国科学院分区表1区
#新刊上线#系列
2024年第一期
2024年第二期
2024年第三期
2024年第四期
2024年第五期
#期刊知识科普#系列
1/ SCI之父尤金·加菲尔德的传奇人生
2/ 国际核心期刊数据库大解析
3/ 手把手教你如何使用最强工具Web of Science
4/ 如何发现一本好期刊
5/ 国内核心期刊有哪些
6/ 版面费与期刊影响力
#精彩文章#系列精选
01/ 城市设计实践发展的多元维度——基于UAL的案例研究
02/ 从智慧城市到共情城市
03/ 传统阿拉伯伊斯兰城市居住区形态学:以传统城市大马士革为例
04/ 建筑遗产预防性保护的意大利视角
05/ 生物与建筑:将科学知识与设计实践相结合的六家法国建筑事务所项目案例研究
06/ 颇具争议的渐进式改造:Elemental建筑事务所金塔蒙罗伊公屋居住区项目的15年
07/ 联合眼动实验和SD法的传统商业街区视觉效果感知评价
08/ 历史的层次:古城堡遗迹中的新建筑改造
09/ 通过空间句法检验帕拉第奥别墅平面中的控制性、中心性和灵活性
10/ 自1931年柯布西耶的Salubra色卡问世后其建筑色彩的偏好:一种跨文化的分析
11/ 建筑师身份的描绘:1920年代末的中国美术建筑师——刘既漂
12/ 探索暴露于风影响下织物的表达与功能
13/ 绿色屋顶能否在地中海气候条件下显著节约能源?基于不同案例的批判性评估
14/ 芬兰近期落成的原木建筑的建构及建筑品质:相关建筑师的解读
15/ 新加坡高校教室光环境品质研究
期刊联络
高等教育出版社: 010-58556484
东南大学:025-83795543
刊物邮箱:foar@pub.seu.edu.cn
FoAR英文期刊交流QQ群:21608832
在线投稿
www.editorialmanager.com/foar
刊物主页
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/20952635
http://journal.hep.com.cn/foar
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、
、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。