2023年5月11日出版的《细胞》杂志发表了美国科学家的一项最新研究成果。来自索尔克生物研究所的Fred H. Gage等研究人员合作开发出研究人类小胶质细胞表型的体内神经免疫类器官模型。
研究人员表示,小胶质细胞是专门驻扎在大脑中的巨噬细胞,在大脑发育、平衡和疾病中发挥着关键作用。然而,直到现在,模拟人类大脑环境和小胶质细胞之间相互作用的能力还受到严重限制。
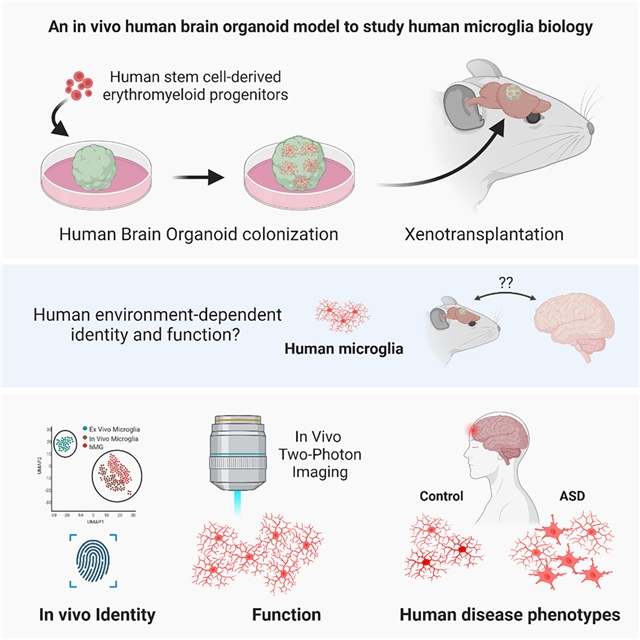
为了克服这些限制,研究人员开发了一种体内异种移植方法,使其能够研究功能成熟的人类小胶质细胞(hMG),这些小胶质细胞在生理上相关的、有血管的免疫能力人脑类器官(iHBO)模型中运作。这些数据显示,居住在类器官中的hMG获得了人类特有的转录组特征,与它们在体内的对应物非常相似。体内双光子成像显示,hMG积极参与监视人类大脑环境,对局部损伤作出反应,并对全身性炎症线索作出反应。最后,研究人员证明,这个移植的iHBO为研究健康和疾病中的功能性人类小胶质细胞表型提供了前所未有的机会,并为自闭症患者特异性模型中的脑环境诱导的免疫反应提供了实验证据。
附:英文原文
Title: An in vivo neuroimmune organoid model to study human microglia phenotypes
Author: Simon T. Schafer, Abed AlFatah Mansour, Johannes C.M. Schlachetzki, Monique Pena, Saeed Ghassemzadeh, Lisa Mitchell, Amanda Mar, Daphne Quang, Sarah Stumpf, Irene Santisteban Ortiz, Addison J. Lana, Clara Baek, Raghad Zaghal, Christopher K. Glass, Axel Nimmerjahn, Fred H. Gage
Issue&Volume: 2023/05/11
Abstract: Microglia are specialized brain-resident macrophages that play crucial roles in brain development, homeostasis, and disease. However, until now, the ability to model interactions between the human brain environment and microglia has been severely limited. To overcome these limitations, we developed an in vivo xenotransplantation approach that allows us to study functionally mature human microglia (hMGs) that operate within a physiologically relevant, vascularized immunocompetent human brain organoid (iHBO) model. Our data show that organoid-resident hMGs gain human-specific transcriptomic signatures that closely resemble their in vivo counterparts. In vivo two-photon imaging reveals that hMGs actively engage in surveilling the human brain environment, react to local injuries, and respond to systemic inflammatory cues. Finally, we demonstrate that the transplanted iHBOs developed here offer the unprecedented opportunity to study functional human microglia phenotypes in health and disease and provide experimental evidence for a brain-environment-induced immune response in a patient-specific model of autism with macrocephaly.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.04.022
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00418-X
