广州实验室Suneng Fu研究团队近期取得重要工作进展,他们研究实现了肌肉反应速率和脂质周转动力学的全局测定。相关研究成果2023年4月4日在线发表于《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
据介绍,代谢是生命的基础,但测量代谢反应率仍然具有挑战性。
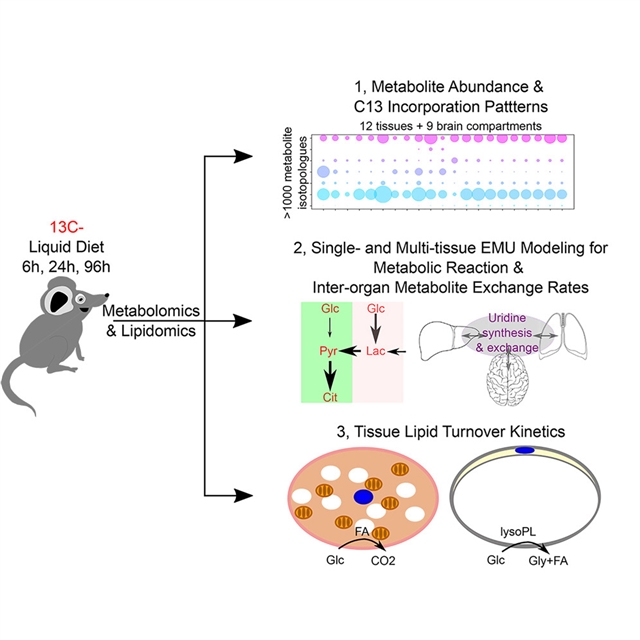
研究人员应用C13通量组学在4天的时间内监测12个组织、9个脑区和1000多个代谢产物等位异构体中的膳食葡萄糖碳代谢。通过基本代谢产物单元(EMU)建模确定了围绕中心碳代谢的85个反应的速率。乳酸氧化,而不是糖酵解,以与三羧酸循环(TCA)相当的速度发生,支持乳酸作为主要燃料。
研究人员扩展了EMU框架,以跟踪和量化跨组织的代谢物流动。具体来说,尿苷代谢的多器官EMU模拟表明,控制核苷酸稳态的是组织血液交换,而不是合成。相反,同位素体指纹图谱和动力学分析显示棕色脂肪组织 (BAT) 具有最高的棕榈酸酯合成活性,但对循环没有明显贡献,表明组织自主合成燃烧机制。
总之,这项研究证明,膳食通量组学在体内动力学映射中的实用性,并为阐明器官间代谢交流机理提供了丰富的资源。
附:英文原文
Title: Global determination of reaction rates and lipid turnover kinetics in Mus musculus
Author: Qishan Chen, Hu Li, He Tian, Sin Man Lam, Yilie Liao, Ziyin Zhang, Manyuan Dong, Shaoru Chen, Yuxiao Yao, Jiemiao Meng, Yong Zhang, Lemin Zheng, Zhuo-Xian Meng, Weiping Han, Guanghou Shui, Dahai Zhu, Suneng Fu
Issue&Volume: 2023/04/04
Abstract: Metabolism is fundamental to life, but measuring metabolic reaction rates remainschallenging. Here, we applied C13 fluxomics to monitor the metabolism of dietary glucosecarbon in 12 tissues, 9 brain compartments, and over 1,000 metabolite isotopologuesover a 4-day period. The rates of 85 reactions surrounding central carbon metabolismare determined with elementary metabolite unit (EMU) modeling. Lactate oxidation,not glycolysis, occurs at a comparable pace with the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA),supporting lactate as the primary fuel. We expand the EMU framework to track and quantifymetabolite flows across tissues. Specifically, multi-organ EMU simulation of uridinemetabolism shows that tissue-blood exchange, not synthesis, controls nucleotide homeostasis.In contrast, isotopologue fingerprinting and kinetic analyses reveal the brown adiposetissue (BAT) having the highest palmitate synthesis activity but no apparent contributionto circulation, suggesting a tissue-autonomous synthesis-to-burn mechanism. Together,this study demonstrates the utility of dietary fluxomics for kinetic mapping in vivo and provides a rich resource for elucidating inter-organ metabolic cross talk.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.007
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(23)00085-2
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
