|
|
| FMD | 前沿研究:CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117bri原始细胞相关基因表达在t(8;21)急性髓系白血病中的临床意义 |
|
论文标题:Clinical significance of CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117brimyeloblast-associated gene expression in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia
期刊:Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Xueping Li, Yuting Dai, Bing Chen, Jinyan Huang, Saijuan Chen, Lu Jiang
发表时间:23 Sep 2021
DOI:10.1007/s11684-021-0836-7
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院李雪萍、代雨婷和姜璐等在Frontiers of Medicine发表研究论文《CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117bri原始细胞相关基因表达在t(8;21)急性髓系白血病中的临床意义》(Clinical significance of CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117brimyeloblast-associated gene expression in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia)。
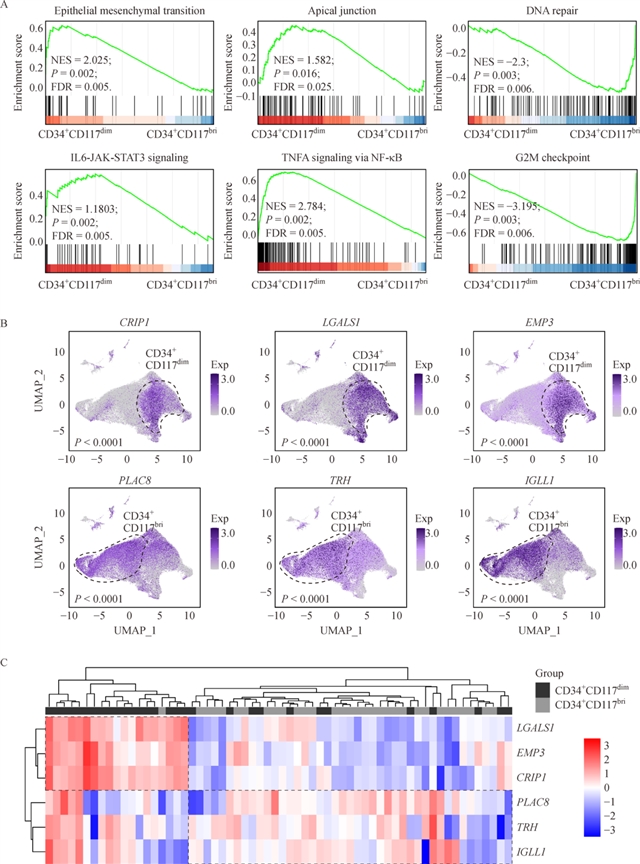
伴t(8;21)(q22;q22)的急性髓系白血病(AML)是一类恶性血液增殖性疾病。在我们前期的研究中,通过单细胞RNA测序、转录组学测序、形态及免疫表型分析等手段,我们发现了两群阻滞于不同阶段的异质性原始细胞群体CD34+CD117dim和CD34+CD117bri,通过研究发现CD34+CD117dim细胞位于髓系分化早期阶段,表现为粒-单核祖细胞标志物的高表达,并呈现白血病干细胞特征。正常造血和细胞分化被认为严格依赖于血液转录调控系统,而异质细胞群体中异常高表达的基因可能导致这些细胞的异常表型。我们的研究从t(8;21) AML的细胞异质性出发,探索了CD34+CD117dim和CD34+CD117bri细胞群体高表达基因与t(8;21) AML预后的相关性,发现LGALS1、EMP3、CRIP1、TRH和PLAC8可作为潜在的预后指标,为今后t(8;21) AML患者的临床预后判断、靶向治疗及机制探索提供新的参考。
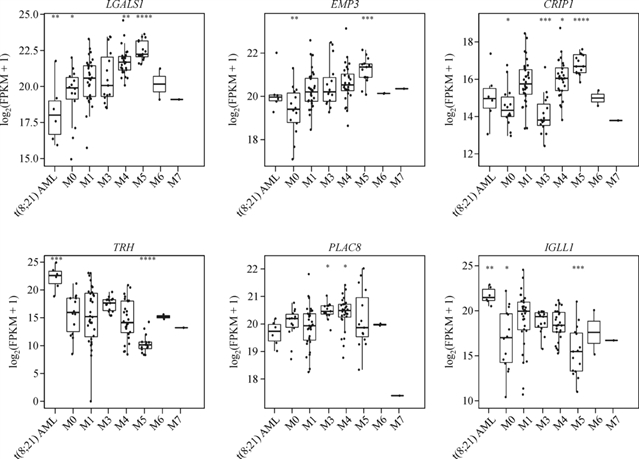
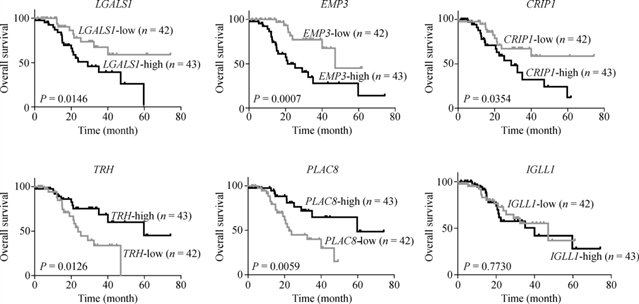
摘 要t(8;21)(q22;q22) 急性髓系白血病(AML)是一类异质性程度较高的血液系统恶性肿瘤。本课题组前期在t(8;21) AML中发现了两群异质性的白血病原始细胞群体:CD34+CD117dim和CD34+CD117bri,其中,CD34+CD117dim细胞比例为t(8;21) AML的独立预后因素。在此基础上,我们对CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117bri细胞相关基因表达情况在t(8;21) AML中的预后影响展开了研究。本研究共招募了85名t(8;21) AML患者,使用实时定量逆转录PCR分析了CD34+CD117dim相关基因(LGALS1、EMP3和CRIP1)以及CD34+CD117bri相关基因(TRH、PLAC8和IGLL1)的mRNA表达水平,并使用Cox回归模型确定基因表达与临床预后之间的关联。结果显示,LGALS1、EMP3或CRIP1高表达患者的总体生存率(OS)显著较差,而TRH或PLAC8高表达的患者预后相对较好。单因素分析显示,CD19、CD34+CD117dim比例、KIT基因突变、微小残留病(MRD)以及LGALS1、EMP3、CRIP1、TRH和PLAC8的表达水平与OS相关。多因素分析显示,KIT基因突变、MRD、CRIP1和TRH表达水平是OS的独立危险因素。CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117bri原始细胞相关基因表达可为t(8;21)AML的预后判断提供新的临床参考。
原文信息
标题Clinical significance of CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117brimyeloblast-associated gene expression in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia
作者Xueping Li, Yuting Dai, Bing Chen, Jinyan Huang, Saijuan Chen, Lu Jiang
机构
1. Shanghai Institute of Hematology, State Key Laboratory of Medical Genomics, National Research Center for Translational Medicine at Shanghai, Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
2. School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
Corresponding AuthorLu Jiang
Cite this article
Xueping Li, Yuting Dai, Bing Chen, Jinyan Huang, Saijuan Chen, Lu Jiang. Clinical significance of CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117brimyeloblast-associated gene expression in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Med., 2021, 15(4): 608–620https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-021-0836-7
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-021-0836-7
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-021-0836-7
摘要
t(8;21)(q22;q22) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a highly heterogeneous hematological malignancy with a high relapse rate in China. Two leukemic myeloblast populations (CD34+CD117dimand CD34+CD117bri) were previously identified in t(8;21) AML, and CD34+CD117dimcell proportion was determined as an independent factor for this disease outcome. Here, we examined the impact of CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117brimyeloblast-associated gene expression on t(8;21) AML clinical prognosis. In this study, 85 patients with t(8;21) AML were enrolled. The mRNA expression levels of CD34+CD117dim-associated genes (LGALS1, EMP3,andCRIP1) and CD34+CD117bri-associated genes (TRH, PLAC8, andIGLL1) were measured using quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Associations between gene expression and clinical outcomes were determined using Cox regression models. Results showed that patients with highLGALS1, EMP3, orCRIP1expression had significantly inferior overall survival (OS), whereas those with high TRH or PLAC8 expression showed relatively favorable prognosis. Univariate analysis revealed that CD19, CD34+CD117dim proportion, KIT mutation, minimal residual disease (MRD), and expression levels ofLGALS1, EMP3, CRIP1,TRHandPLAC8were associated with OS. Multivariate analysis indicated thatKITmutation, MRD andCRIP1andTRHexpression levels were independent prognostic variables for OS. Identifying the clinical relevance of CD34+CD117dim/CD34+CD117brimyeloblast-associated gene expression may provide new clinically prognostic markers for t(8;21) AML.

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、 、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。