|
|
| FESE | 前沿动态:Best Papers of 2021! |
|
论文标题:前沿动态:Best Papers of 2021!
期刊:Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
发表和传播优质研究成果是科技期刊的天然使命。作为中国科技期刊卓越行动计划重点期刊、中国工程院院刊系列,FESE一直致力于提升发文质量,同时也通过评选年度“Best Papers”等活动,以肯定优质学术成果、促进环境领域的理论和技术创新。
2021年,FESE共发表133篇研究和综述论文。编委会组织评选出3篇Best Papers,现予以公布。

2021年度FESE期刊Best Papers信息如下:
(点击阅读详情)
文章信息
Evaluation of the technoeconomic feasibility of electrochemical hydrogen peroxide production for decentralized water treatment
Yang Li, Yixin Zhang, Guangshen Xia, Juhong Zhan, Gang Yu, Yujue Wang
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15(1): 1.
doi. 10.1007/s11783-020-1293-2
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fese/EN/10.1007/s11783-020-1293-2
微信推文
FESE: 清华大学王玉珏教授研究团队 电化学产过氧化氢在分散式水处理应用中的技术经济可行性分析
文章点评
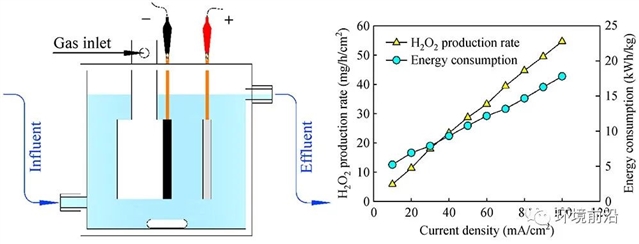
On-site and on-demand production of H2O2 in an energy-efficient, environmental friendly, and safe way is of great significance to advanced oxidation processes in wastewater treatment. This study evaluated the techno-economic feasibility of H2O2 production from oxygen reduction at a gas diffusion cathode under long-term realistic operating conditions. The electrochemical cell with carbon black-polytetrafluoroethylene electrodes achieved apparent current efficiencies of > 80% over a wide current densities of 5 to 400 mA/cm2, and a steady performance during a test period of 46 days. Enhanced abatement of ozone-resistant micro-pollutants was achieved when combining the H2O2 production cell with ozonation. The preliminary overall cost of electrochemical H2O2 production was estimated to be ~0.88 $/kg. This study confirmed that on-site electrochemical H2O2 production with gas diffusion electrode is feasible for practical water treatment.
(点击阅读详情)
文章信息
A “Seawater-in-Sludge” approach for capacitive biochar production via the alkaline and alkaline earth metals activation
Xiling Li, Tianwei Hao, Yuxin Tang, Guanghao Chen
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15(1): 3.
doi. 10.1007/s11783-020-1295-0
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fese/EN/10.1007/s11783-020-1295-0
微信推文
FESE: 澳门大学郝天伟老师研究组 海水活化污泥制备电容性生物炭研究
文章点评
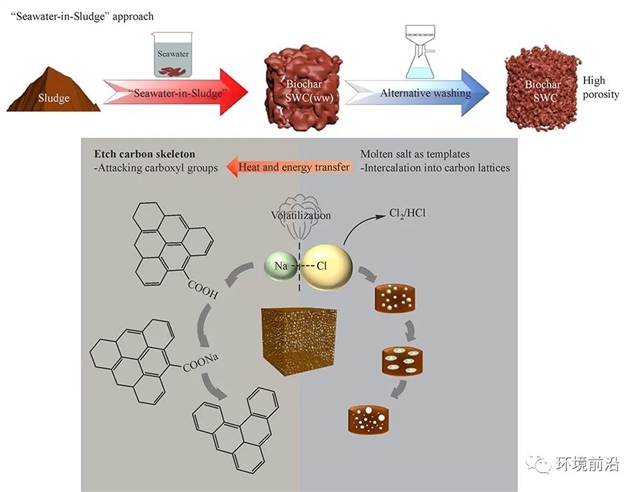
Slow pyrolysis of wasted activated sludge (WAS) to produce biochar has gained broad interest as a new option to recover useful carbon resources beyond biogas from wastewater treatment plants. The activation of biochar in an ecofriendly and economic way to create porous structure and develop porosity is of significance particularly when the generated biochar is used to fabricate electrochemical capacitors. This study proposed conceptually to use sea water for chemical activation to prepare capacitive biochar from WAS, i.e., a “Seawater-in-sludge” approach, and proved it. The experiments proved the feasibility of seawater as an activation agent, and the produced biochar obtained larger surface area (up to 480.3 m2/g) with hierarchical porosity distribution, higher graphitization degree, and less functional groups than the conventional directly-pyrolyzed sludge. The lower resistance, higher specific capacitance (up to 113.9 F/g), excellent durability and stability in the electrochemical tests proved the produced biochar favorable as a capacitive material. The study offered a new cost-effective route for simultaneous WAS treatment and resource recovery especially in coastal areas.
(点击阅读详情)
文章信息
Improved degradation of azo dyes by lignin peroxidase following mutagenesis at two sites near the catalytic pocket and the application of peroxidase-coated yeast cell walls
Karla Ilic Durdic, Raluca Ostafe, Olivera Prodanovic, Aleksandra Durdevic Delmaš, Nikolina Popovic, Rainer Fischer, Stefan Schillberg, Radivoje Prodanovic
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15(2): 19.
doi. 10.1007/s11783-020-1311-4
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fese/EN/10.1007/s11783-020-1311-4
微信推文
FESE: 塞尔维亚学者 木质素过氧化物酶展示在酵母细胞表面实现生物酶固定并用于偶氮染料降解
文章点评
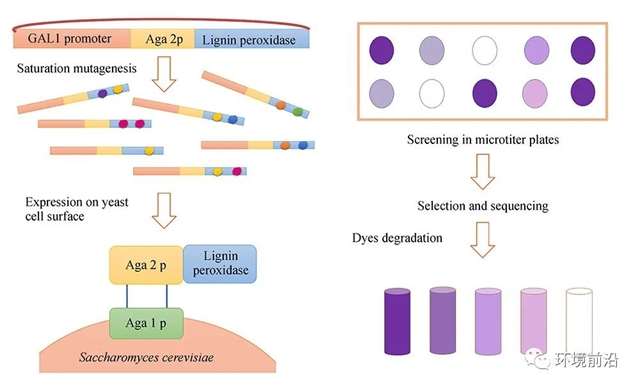
Enzymatic engineering is a promising alternative to effectively degrading azo dyes. This study applied saturation mutagenesis to a wild-type lignin peroxidase (LiP) and screened to identify LiP variants for efficient azo dye degradation, after which a novel biocatalyst was prepared by displaying the mutants on the surface of yeast cell wall fragments. Experiments showed that the mutations improved the overall catalytic activity for three target dyes though the influences on the affinity to the substrate (Km) and the catalytic activity (kcat) were differentiated. Besides, the yeast cell wall fragments with mutated LiP degraded three target dyes at percentages of 85% to 99%, higher than that with wild-type LiP (35% to 60%); and maintained the enzyme activity and stability after ten reaction cycles each lasting 8 h. This study provides a strategy for enzyme improvement to be applied for effective target pollutant removal, and also a means to immobilize the enzyme in a stable and ready-to-use form.
推荐阅读
•FESE: 清华大学王玉珏教授研究团队 电化学产过氧化氢在分散式水处理应用中的技术经济可行性分析
•FESE: 澳门大学郝天伟老师研究组 海水活化污泥制备电容性生物炭研究
•FESE: 塞尔维亚学者 木质素过氧化物酶展示在酵母细胞表面实现生物酶固定并用于偶氮染料降解
•FESE:2022年第5期出版“北美华人环境工程与科学教授协会前沿研究”专刊

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、 、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。