|
|
| FCS | 最新研究:使用迭代神经网络进行嵌套关系抽取 |
|
论文标题:Nested relation extraction with iterative neural network (使用迭代神经网络进行嵌套关系抽取)
期刊:Frontiers of Computer Science
作者:Yixuan CAO, Dian CHEN , Zhengqi XU, Hongwei LI , Ping LUO
发表时间:27 Jan 2021
DOI:10.1007/s11704-020-9420-6
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导读
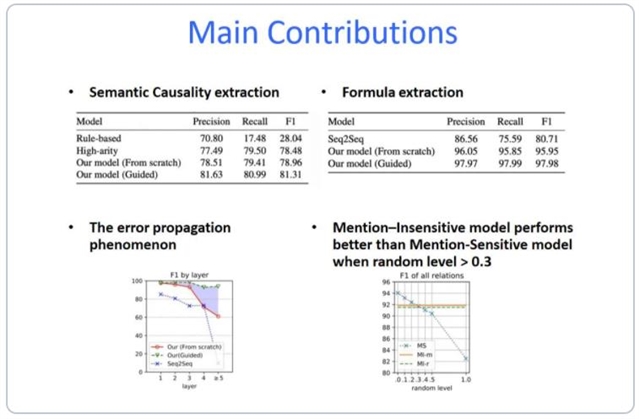
目前的关系抽取研究主要关注实体间的单层二元关系,但是自然语言中很多对于事实的描述是复杂的,特别在对表达的准确性要求较高的专业领域如金融、生物医学等。因此我们提出了嵌套关系抽取的问题,将其形式化定义为有向无环图的结构抽取问题。之后,我们提出了一个迭代的神经网络可以逐层抽取关系结构体。我们提出的方法在两个嵌套关系数据集(语义因果关系、公式关系)上达到了78.98和97.89的F1值。
我们还发现,嵌套关系常常表达在长句中,而对于同一实体常常有多次重复提及,这对标注提出了挑战。因此我们将模型扩展成为了提及不敏感的方法,这样标注就只需要在实体概念级别进行,而不需要指定具体的提及。我们的提及不敏感模型在提及选择的随机性大于0.3后,表现超过提及敏感的模型。
文章精要


摘要
Most existing researches on relation extraction focus on binary flat relations like BornIn relation between a Person and a Location. But a large portion of objective facts described in natural language are complex, especially in professional documents in fields such as finance and biomedicine that require precise expressions. For example, “the GDP of the United States in 2018 grew 2.9% compared with 2017” describes a growth rate relation between two other relations about the economic index, which is beyond the expressive power of binary flat relations. Thus, we propose the nested relation extraction problem and formulate it as a directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure extraction problem. Then, we propose a solution using the Iterative Neural Network which extracts relations layer by layer. The proposed solution achieves 78.98 and 97.89 F1 scores on two nested relation extraction tasks, namely semantic cause-and-effect relation extraction and formula extraction. Furthermore, we observe that nested relations are usually expressed in long sentences where entities are mentioned repetitively, which makes the annotation difficult and errorprone. Hence, we extend our model to incorporate a mentioninsensitive mode that only requires annotations of relations on entity concepts (instead of exact mentions) while preserving most of its performance. Our mention-insensitive model performs better than the mention sensitive model when the random level in mention selection is higher than 0.3.
相关内容推荐:
面向生物医学实体对齐的集成学习模型 2021 15(3):153321
提升面部年龄识别的实用方法 2021 15(3):153318
【FCS 人工智能专栏】面向社交的众包的任务分配 2021 15(2):152316
【FCS 人工智能专栏】知识图谱中的实体集扩展:异质信息网络的视角 2021 15(1):151307
【FCS 人工智能专栏】物联网环境中用户下一步访问位置预测 2021 15(1):151306
【FCS 人工智能专栏】智慧城市中基于稀疏表示模型的时间序列预测框架 2021 15(1):151305
【FCS 人工智能专栏】词翻译在神经网络句子对齐中的应用研究 2021 15(1):151302
【FCS 人工智能专栏】基于点态流形正则化的半监督学习 2021 15(1):151303
【FCS 人工智能专栏】SSDBA:一种基于伸缩距离的社交网络链路预测算法 2021 15(1):151301
【FCS 优秀青年科学家论坛】生物启发的视觉计算 2021 15(1):151304
Frontiers of Computer Science
Frontiers of Computer Science (FCS)是由教育部主管、高等教育出版社和北京航空航天大学共同主办、SpringerNature 公司海外发行的英文学术期刊。本刊于 2007 年创刊,双月刊,全球发行。主要刊登计算机科学领域具有创新性的综述论文、研究论文等。本刊主编为周志华教授,共同主编为熊璋教授。编委会及青年 AE 团队由国内外知名学者及优秀青年学者组成。本刊被 SCI、Ei、DBLP、INSPEC、SCOPUS 和中国科学引文数据库(CSCD)核心库等收录,为 CCF 推荐期刊;两次入选“中国科技期刊国际影响力提升计划”;入选“第4届中国国际化精品科技期刊”;入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划项目”。

长按二维码关注Frontiers of Computer Science公众号
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、 、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
高等教育出版社入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划”集群化项目。Frontier系列期刊中:13种被SCI收录;1种被A&HCI收录;6种被Ei收录;2种被MEDLINE收录;11种中国科技核心期刊;16种被CSCD收录。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。